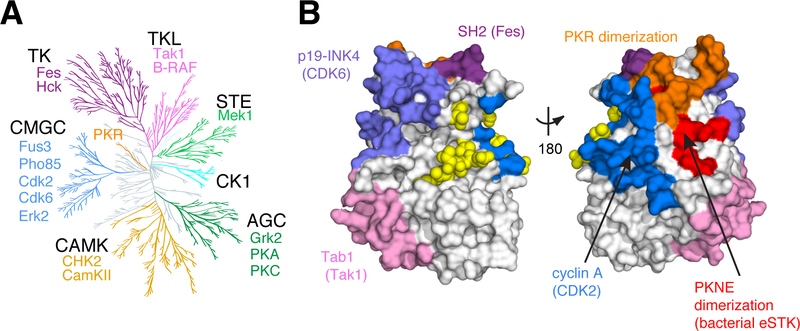
Figure 1. Regulatory Diversity in the Eukaryotic Protein Kinases.
A. Unanchored dendrogram of the human kinome illustrating the diversity of the EPK superfamily and subfamilies. Individual subfamily members with functional mutations shown in Fig. 4c and included in Supplementary Table 7 are listed. TK: tyrosine kinase; TKL: TK-like; STE: STE7/11/20; CK1: Casein Kinase 1; AGC: protein kinase A/G/C; CAMK: Calmodulin kinase; CMGC: cyclin dependent kinase (CDK)/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)/glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)/CDK-like kinase (CLK).
B. Allosteric regulatory sites from diverse kinases mapped to a single representative structure - yeast CDK Pho85 (PDB: 2PK9, shown as space-filled surface). Regulatory surfaces were identified by structural alignment of the kinase of interest to Pho85; all Pho85 positions within 4Å of the interaction surface are colored. Color coding is the same as in (A). Bright yellow spheres indicate known phosphoregulatory sites.