Figure 1.
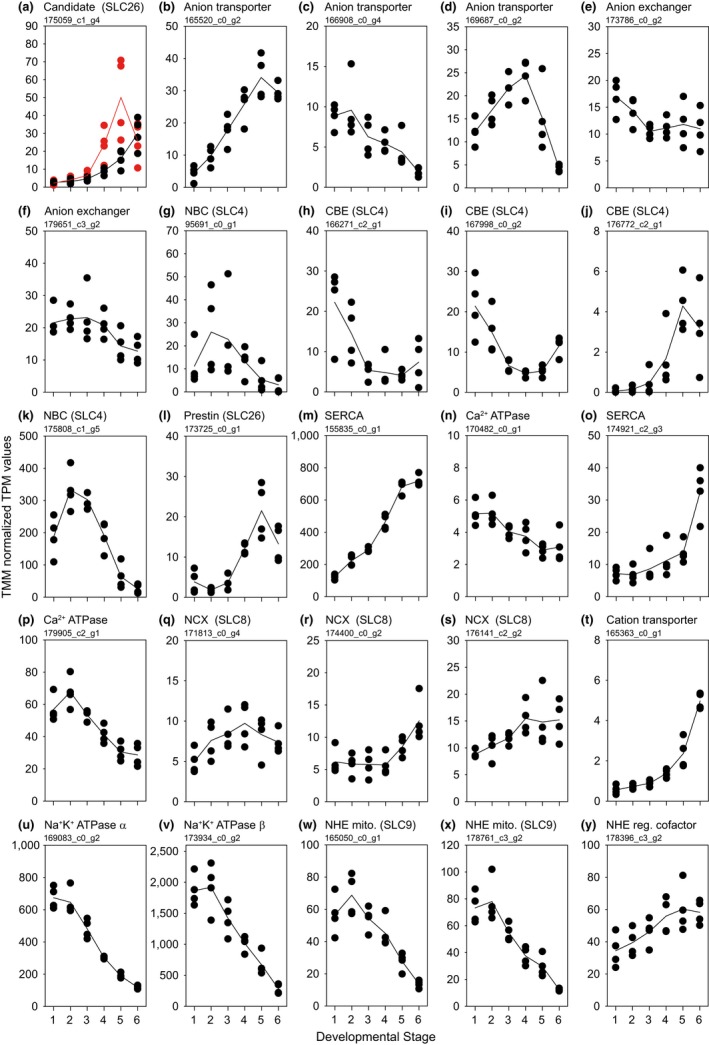
Genes encoding putative ion transport proteins involved in larval calcification in Mytilus edulis. The morphological stages described in Table 1 and Figure S1 are marked as 1–6 on the x‐axes. Expression values for (a) The candidate SLC26 protein identified by the substrate limitation experiment. Expression values for low C T and ambient conditions marked in red in black, respectively. (b–d) Anion transport proteins (e, f) Anion exchange proteins (g, k) A SLC4 sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (h–j) SLC4 chloride‐bicarbonate exchange proteins (l) A SLC26 prestin protein (m, o) Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) proteins (n, p) Calcium‐transporting ATPase proteins (q–s) Sodium‐calcium exchange proteins (t) Cation‐transporting protein (u) Sodium potassium ATPase α subunit (v) Sodium potassium ATPase β subunit (w, x) Mitochondrial isoforms of sodium‐hydrogen exchange (NHE) proteins from SLC9 and (y) Sodium‐hydrogen exchange (NHE) regulatory cofactor. Maximum posterior probability for all contigs is reported in Table S7
