Figure 6.
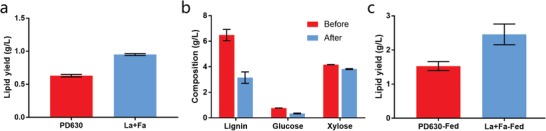
Fermentation of the engineered strain grown on lignin‐containing biorefinery waste from AFEX pretreated corn stover. a) The lipid yield of the consortium of engineered strains by single‐batch fermentation on the lignin‐containing biorefinery waste. PD630: fermentation with the control strain R. opacus PD630 on 1.5% biorefinery waste (w/v) for 4 d; La+Fa: cofermentation by engineered strain R. opacus PD630_La and PD630_Fa on 1.5% biorefinery waste for 4 d. b) The composition analysis of the lignin‐containing biorefinery waste before and after the single‐batch cofermentation by engineered strain PD630_La and PD630_Fa for 4 d. The composition was analyzed according to the Laboratory Analytical Procedure from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass). c) The lipid yield of the engineered strain by fed‐batch fermentation on the lignin‐containing biorefinery waste. PD630‐Fed: fed‐batch fermentation of control strain R. opacus PD630_Fa on 1.5% lignin waste for 6 d; La+Fa‐Fed: fed‐batch cofermentation of R. opacus PD630_La and PD630_Fa on 1.5% lignin waste for 6 d.
