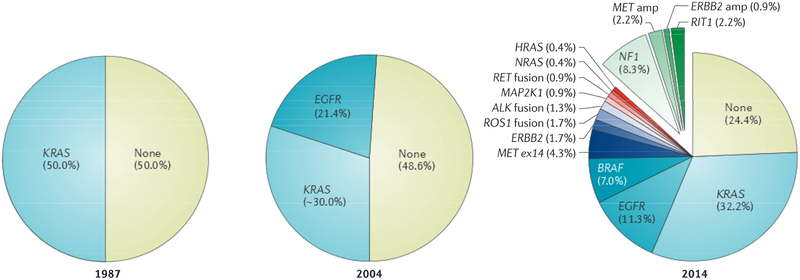
Figure 3|. Knowledge of non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma has evolved in recent decades.
Traditionally, lung cancer was grouped by histology into small cell lung cancer and non-small cell squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma. In 1987, a KRAS mutation was identified in ~25% of all non-small cell lung cancers, and 50% of lung adenocarcinomas22. In 2004, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations were identified as an additional mutation in lung adenocarcinomas23. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Network’s next-generation sequencing of lung adenocarcinoma in 2014 led to the identification of more than 15 different gene events that could be exploited for treatment and/or used for subclassifying patients into new taxa7. ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; amp, amplification; ex, exon; RIT1, Ras like without CAAX1. Data in the left panel were abstracted from Rodenhuis et al.22. Data in the middle panel were abstracted from Paez et al23 and Riley et al.132. The right panel of the figure is from REF. 7, Nature Publishing Group.