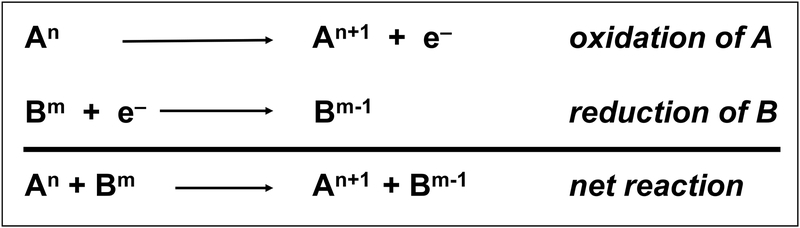
Figure 1.
Basic scheme of oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Molecule A loses an electron and becomes oxidized while molecule B accepts an electron and becomes reduced. Thus, the net reaction is simply the transfer of the electron from molecule A to molecule B. In the illustration, “n” and “m” refer to the oxidation state of molecules A and B, respectively. When electrons are lost, the oxidation number increases (An+1). Conversely, when electrons are gained, the oxidation number decreases (Bm−1).