Figure 7.
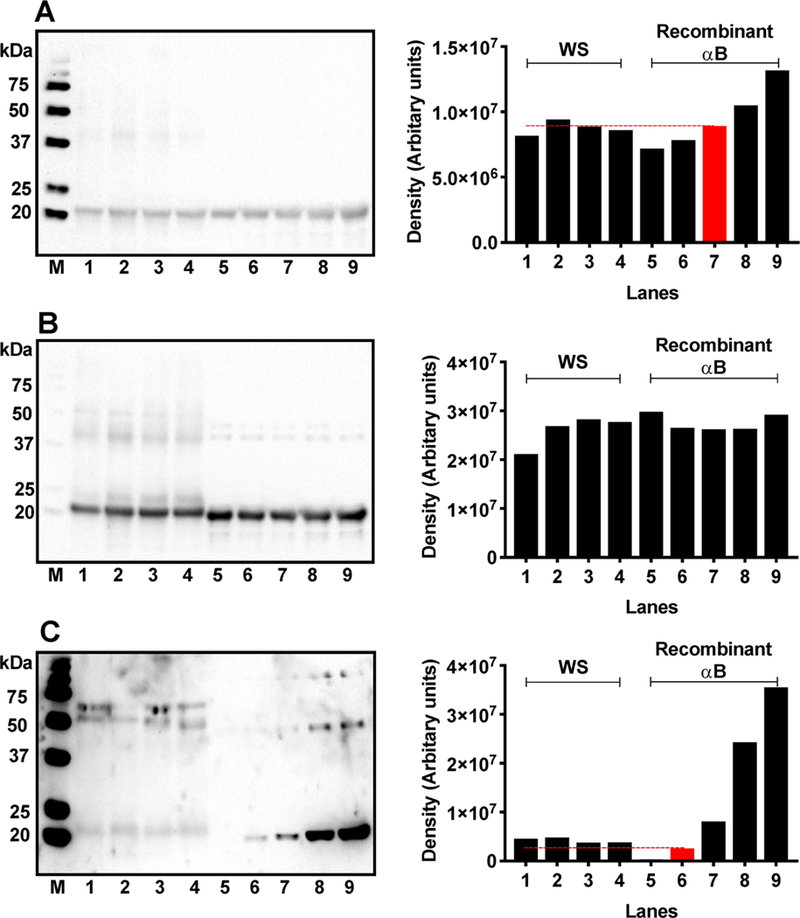
Succinylation of αB in vitro compared to the level of succinylation of αB-crystallin in human lenses. Quantitative comparison of αB levels in the WS from 9-, 23-, 46,-and 71-year-old lenses with the recombinant αB (A). M, molecular weight markers; lanes 1–4, 20 μg of WS from 9-, 23-, 46-, and 71-year-old lenses; lanes 5–9, recombinant αB at 1,1.5,2,2.5, and 3 μg of protein. Densitometric analysis in the right panel shows that 20 μg of WS contains ~2 μg of αB (red bar). Recombinant αB was then succinylated in vitro with increasing concentrations of SuccCoA and then compared with succinylated αB in human lenses. Western blot of WS and succinylated recombinant αB was performed and probed with a monoclonal antibody against αB-crystallin (B) and then reprobed for SuccK (C). The succinylation of αB in vitro was performed using various molar concentrations of SuccCoA relative to the lysine content in αB (see below). The red bar indicates succinylation of αB to an almost similar extent to that of αB-crystallin in human lenses. M, molecular weight markers; lanes 1–4, WS from 9-, 23-, 46-, and 71-year-old lenses; 5, recombinant αB control; 6–9, succinylated recombinant αB generated at αB/SuccCoA molar ratios of 1:0.001, 1:0.003, 1:0.007, and 1:0.01, respectively. Right panels are the densitometric analysis of the respective Western Blots in the left panels. The dashed line in panel C indicates the density of Succ-αB (red) (1:0.001) relative to the succinylated αB-crystallin in human lenses.
