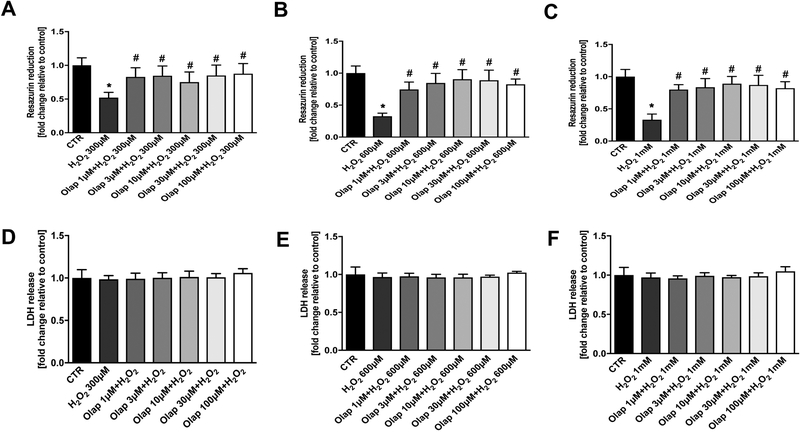
Figure 25. Effect of olaparib on cellular viability in U937 cells subjected to H2O2-induced oxidative stress in vitro.
(A): Effect of olaparib on cellular resazurin reduction in control cells (without oxidative stress challenge) and in cells subjected to oxidative (H2O2) in the presence of various concentrations of olaparib. Cells were treated with olaparib (1, 3, 10, 30 or 100 μM), followed immediately by 300 μM H2O2 for 1 hour. Data are shown as mean±SEM of n=3 determinations. *p<0.05 shows significant decrease in resazurin conversion in response to H2O2, compared to control cells; #p<0.05 shows significant protective effect of olaparib in H2O2 challenged cells compared to vehicle-treated H2O2 challenged cells. (B): Effect of olaparib on LDH content (a marker of cell necrosis) in the supernatant of control cells (without oxidative stress challenge) and in cells subjected to oxidative (H2O2) in the presence of various concentrations of olaparib. Cells were treated with olaparib (1, 3, 10, 30 or 100 μM), followed immediately by 300 μM H2O2 for 1 hour. Data are shown as mean±SEM of n=3 determinations.