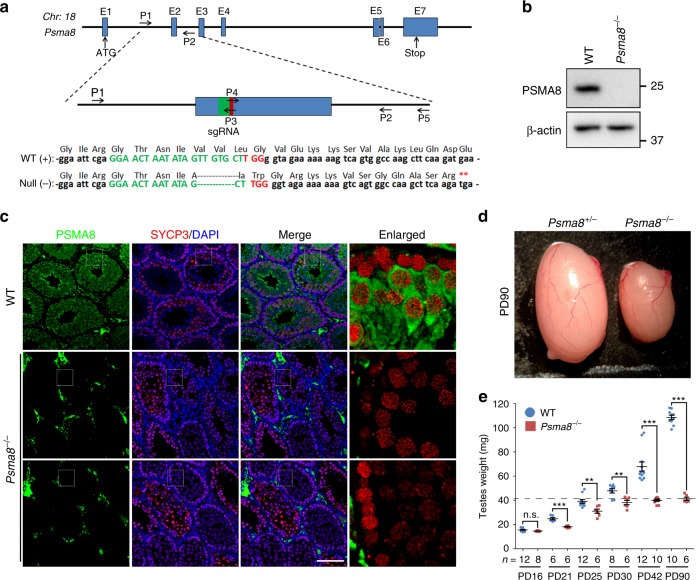
Fig. 2.
PSMA8 is required for male fertility. a Schematic diagram showing the gene structure of Psma8 and the CRISPR/Cas9 strategy used to generate the knockout allele. The null allele of Psma8 harbored a 5-bp deletion within the selected single-guide RNA (sgRNA) and introduced a premature stop codon (**). The locations of sgRNA and primers (P1–P5) are indicated. The primer sequences are provided in Supplementary Table 1. b, c Western blotting (b) and immunofluorescent staining (c) showing successful deletion of PSMA8 in spermatocytes at PD42. Scale bar, 100 μm. d A representative image showing the morphology of testes derived from Psma8+/− and Psma8−/− males at the age of PD90. “+” represents the wild-type (WT) allele. e Weights of testes derived from WT and Psma8−/− males at the indicated ages. n = 6 testes for both WT and Psma8−/− at PD21, and Psma8−/− at PD25, PD30 and PD90; n = 8 testes for WT at PD30 and Psma8−/− at PD16; n = 10 testes for WT at PD90 and Psma8−/− at PD42; n = 12 testes for WT at PD16, PD25, and PD42. Error bars indicate S.E.M. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t tests. n.s. not significant. The dashed line shows the weight of knockout testes at the age of PD90