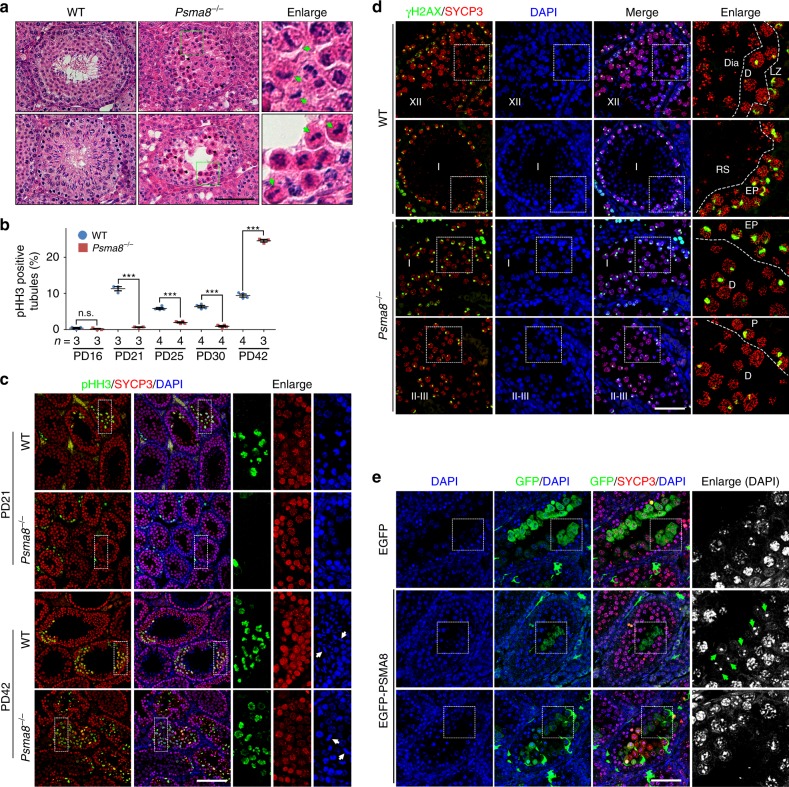
Fig. 6.
PSMA8 deletion causes delayed M-phase entry and M-phase arrest. a Hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) staining of testes derived from wild-type (WT) and Psma8−/− males. Some metaphase cells are enlarged on the right and indicated with arrows. Scale bar, 50 μm. b Percentage of seminiferous tubules containing spermatocytes positive for phosphorylated Histone H3 (pHH3). n = 3 sections for both WT and Psma8−/− testes at PD16 and PD21, and Psma8−/− testes at PD42; n = 4 sections for both WT and Psma8−/− testes at PD25 and PD30, and WT testes at PD42. Error bars indicate S.E.M. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t tests. n.s. not significant. c Staining of pHH3 on testes sections derived from WT and Psma8−/− males at PD21 and PD42. Arrows indicate metaphase cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. d Staining of phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) in testes sections derived from WT and Psma8−/− males at PD42. The stages of seminiferous tubules are indicated. Scale bar, 50 μm. e Overexpression of PSMA8 partially rescued spermatogenesis defects. Green arrows indicate round spermatids. Scale bar, 50 μm