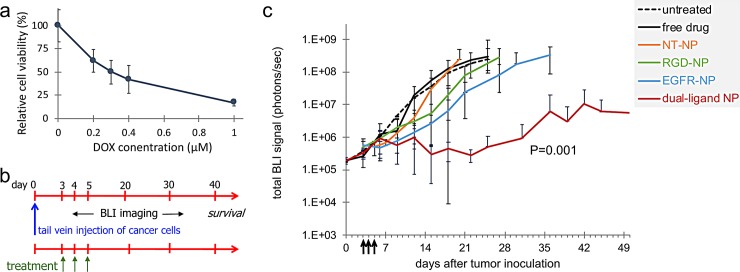
Fig 3. Treatment of mice with D2.A1 metastasis using dual-ligand nanoparticle loaded with doxorubicin.
(a) The cytotoxicity of doxorubicin (DOX) was evaluated on D2.A1 cells. Cytotoxicity studies were performed by seeding D2.A1 cells at a density of 5 x 103 cells per well. Cells were incubated with the treatment for 24 h at a concentration ranging between 0.2–1 μM DOX. After treatment application, the cells were washed three times with fresh medium and then incubated for 48 h at 37°C. The number of viable cells was determined using a formazan-based cell counting assay (CCK-8). Untreated cells served as live controls for normalization of the data. Data points represent group mean ± s.d. (b) The timeline and schedule of treatments are shown with respect to tumor inoculation. (c) The response of cancer metastasis to treatment was monitored using longitudinal BLI imaging. Quantification of the BLI signal in the thoracic region is shown for mice with D2.A1 metastasis treated at days 3, 4 and 5. In addition to untreated animals, treatments included non-targeted NP (NT-NP), RGD-NP, EGFR-NP, dual-ligand NP, and free DOX (n = 6–8 mice per treatment). The y-axis is in logarithmic scale. All nanoparticle formulations were administered at 7.5 mg/kg DOX (two-way ANOVA with repeated measures).