Fig. 4.
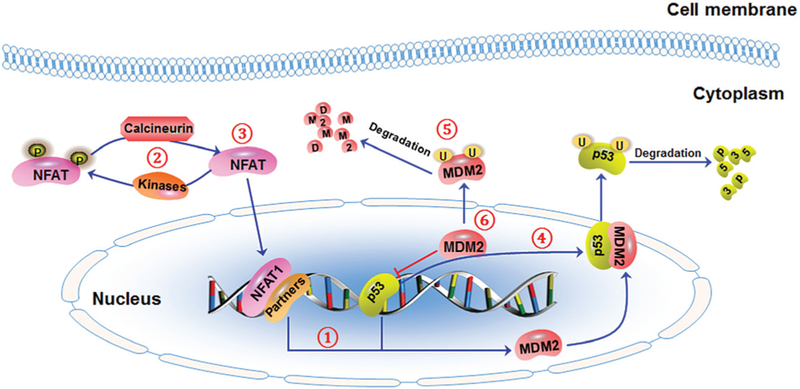
The schematic diagram illustrates targeting strategies for the NFAT1-MDM2-p53 pathway. To effectively inhibit NFAT1’s expression and activity, three targeting strategies have been proposed: (1) blocking NFAT1-MDM2 DNA binding, (2) promoting NFAT1 phosphorylation and/or inhibiting NFAT1 dephosphorylation, and (3) directly destabilizing NFAT1 protein. To effectively inhibit MDM2’s expression and activity, three targeting strategies have been proposed: (4) blocking MDM2-p53 interaction, (5) promoting MDM2 autoubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, and (6) directly inhibiting MDM2 expression. Small molecules that can dually inhibit NFAT1-MDM2 may be developed using these targeting strategies.
