Figure 2. Genome-wide fixation index (FST) and Pooled Heterozygosity (Hp) analyses across the fox genome.
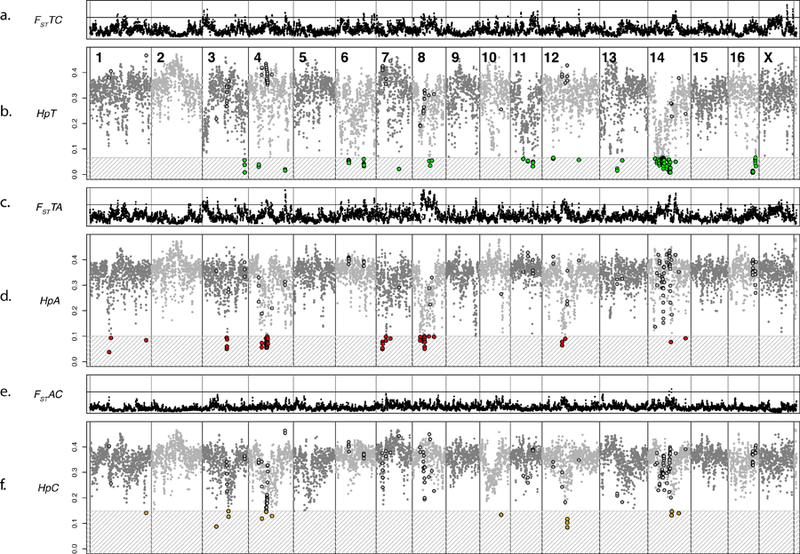
Dots on all panels represent the 500-kb windows analyzed in both the FST and Hp analyses. The order of the windows is based on the LASTZ mapping of individual windows to the dog genome and the previously published fox/dog synteny map (chimeric scaffolds are split to reflect the most likely location of each window in the fox genome). Gray vertical lines separate fox chromosomes. Chromosome numbers are indicated in panel b. Panels a, c, and e: FST analysis across the fox genome. The horizontal line is FST =0.458. Panels b, e, and f: Hp analysis across the fox genome. The gray patterned box and colored dots indicate the windows that reached significance in that population (Supplementary Table 6; Supplementary Figure 11). The dots that are outlined in the non-significant zones are windows that reached significance in a different population. a. FST between the tame and conventional populations. b. Hp in the tame population. c. FST between tame and aggressive populations. d. Hp in the aggressive population. e. FST between aggressive and conventional populations. f. Hp in the conventional population.
