Fig. 4.
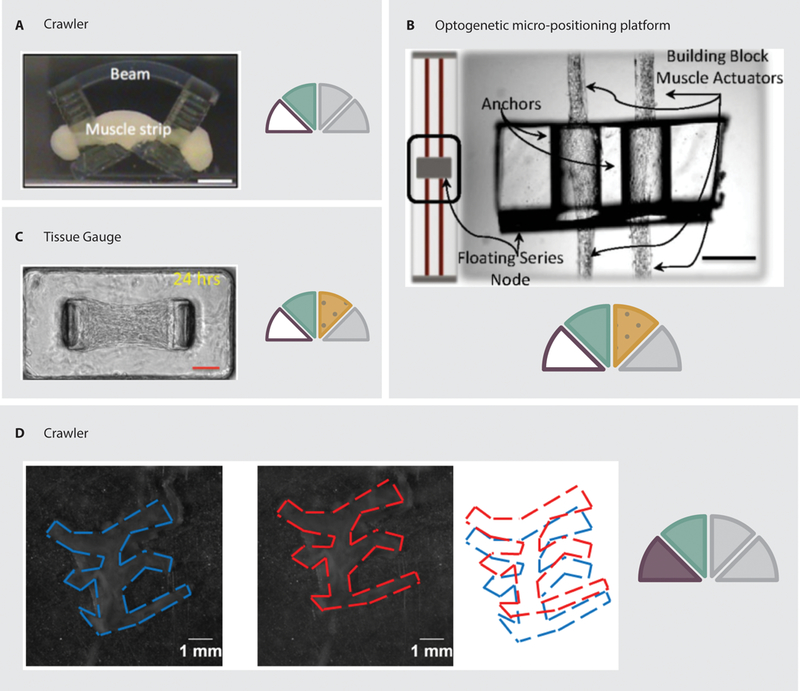
Examples of skeletal muscle powered devices. A: A crawling device driven by contraction of a cell/gel tissue construct supported by a 3D printed structure (45). B: A micro-positioning platform suspended by optogenetically modified cell/gel muscle actuators, which allow the position and rotation of the platform to be controlled via light stimuli (44). C: A stationary culture system in which cells are seeded in a gel mixture around flexible pillars. Deflection of the pillars allows the contraction force to be calculated (43). D: A completely organic device using electrocompacted and aligned collagen as a substrate (21).
