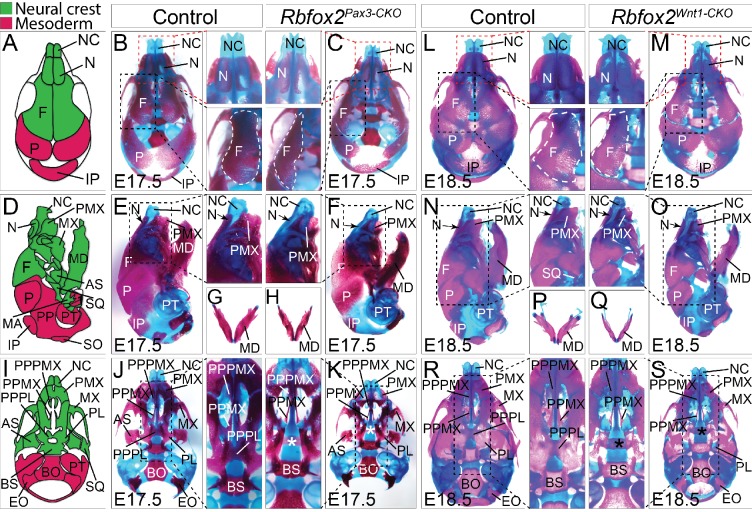
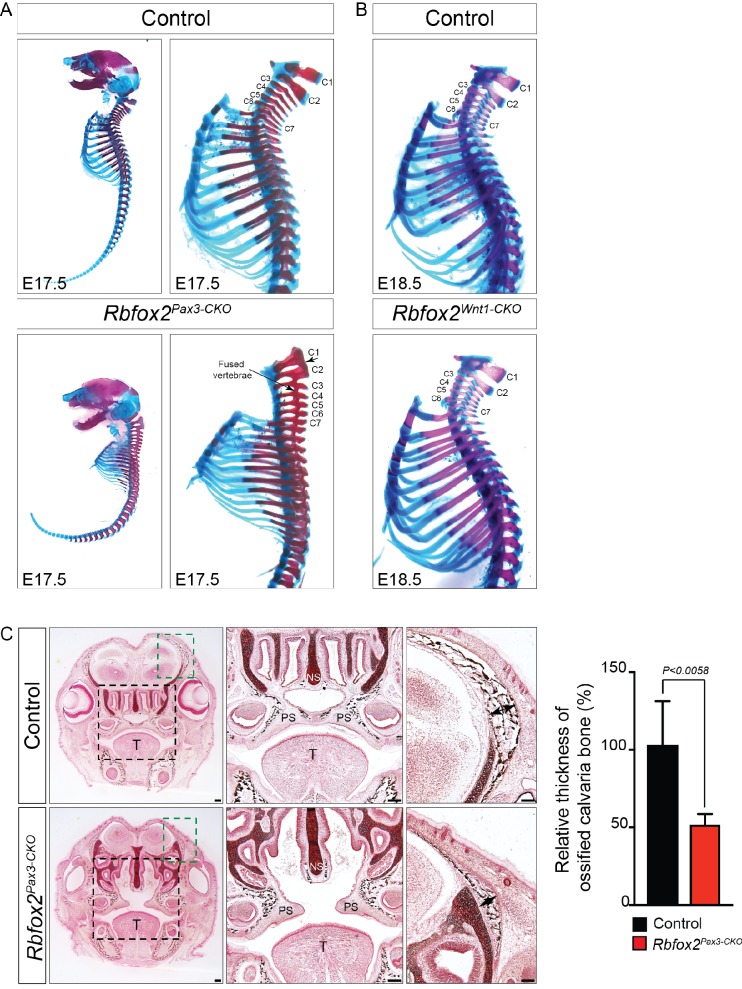
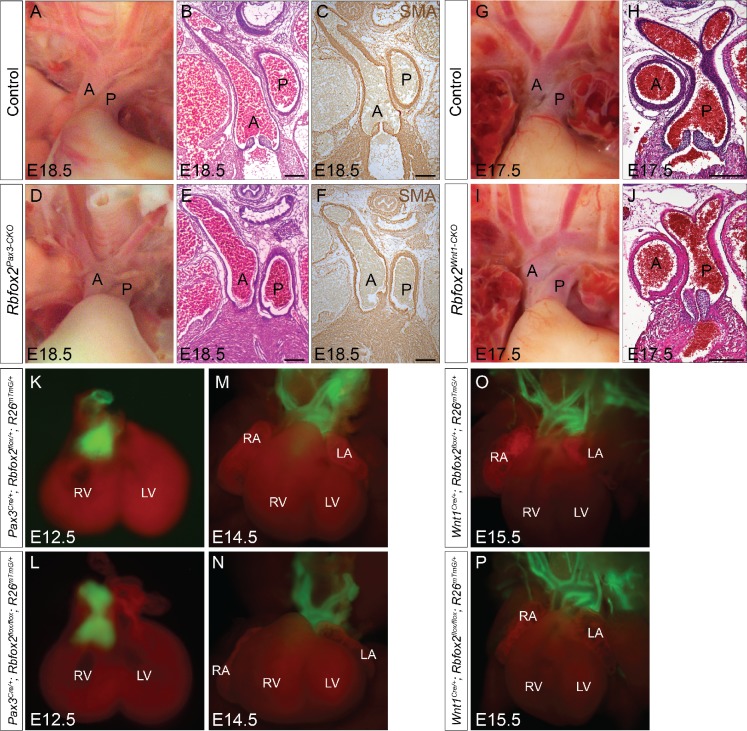
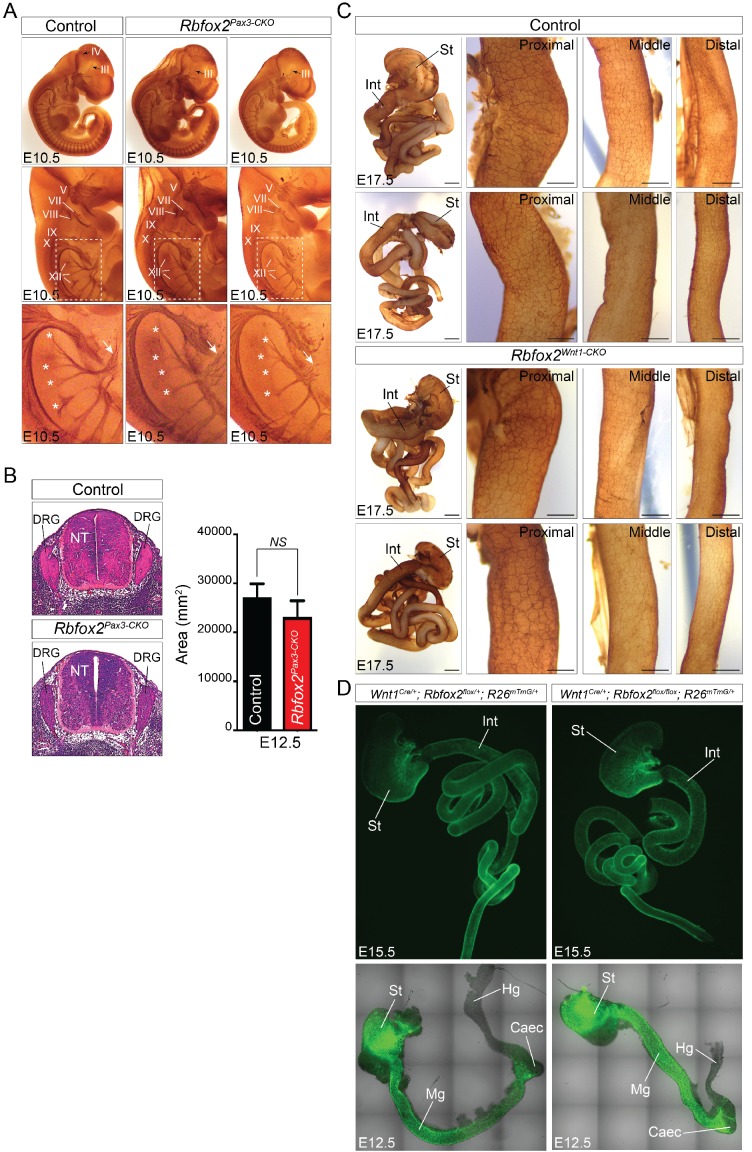
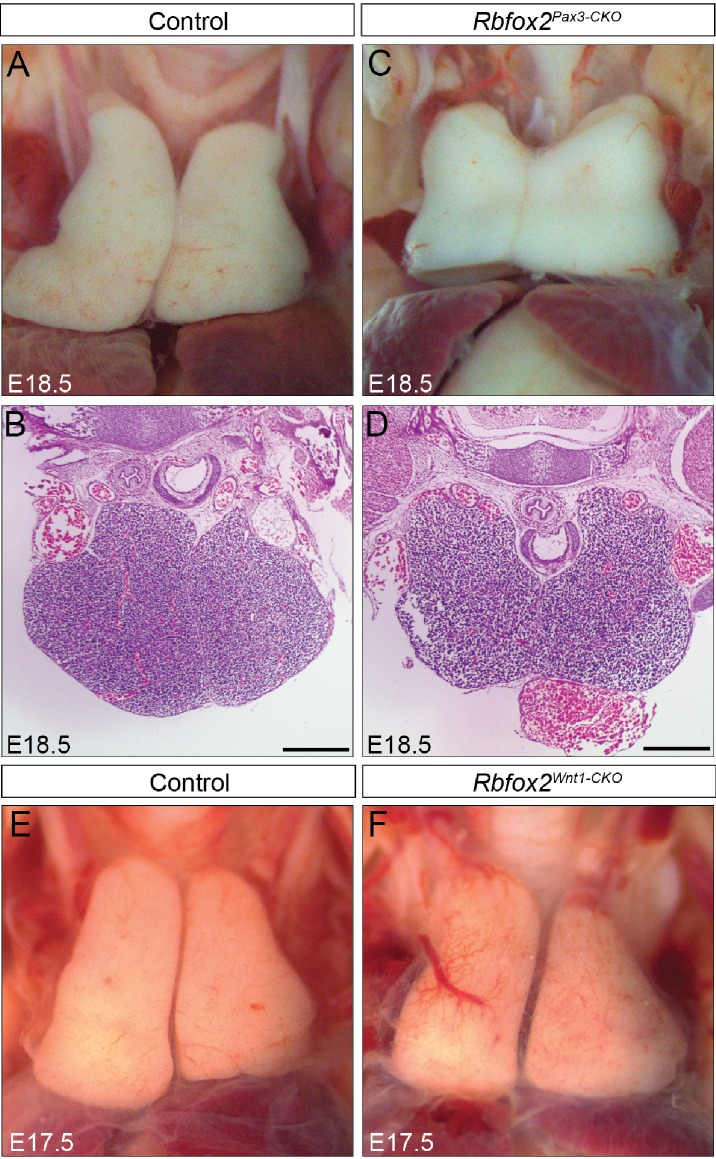
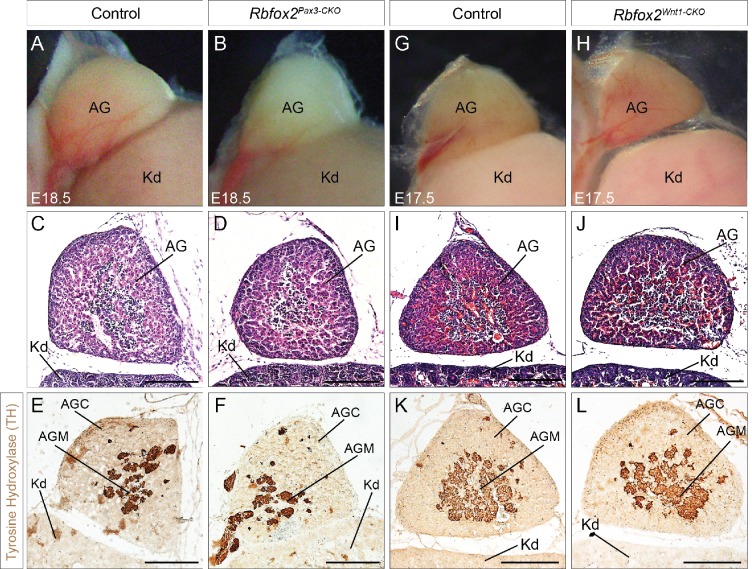
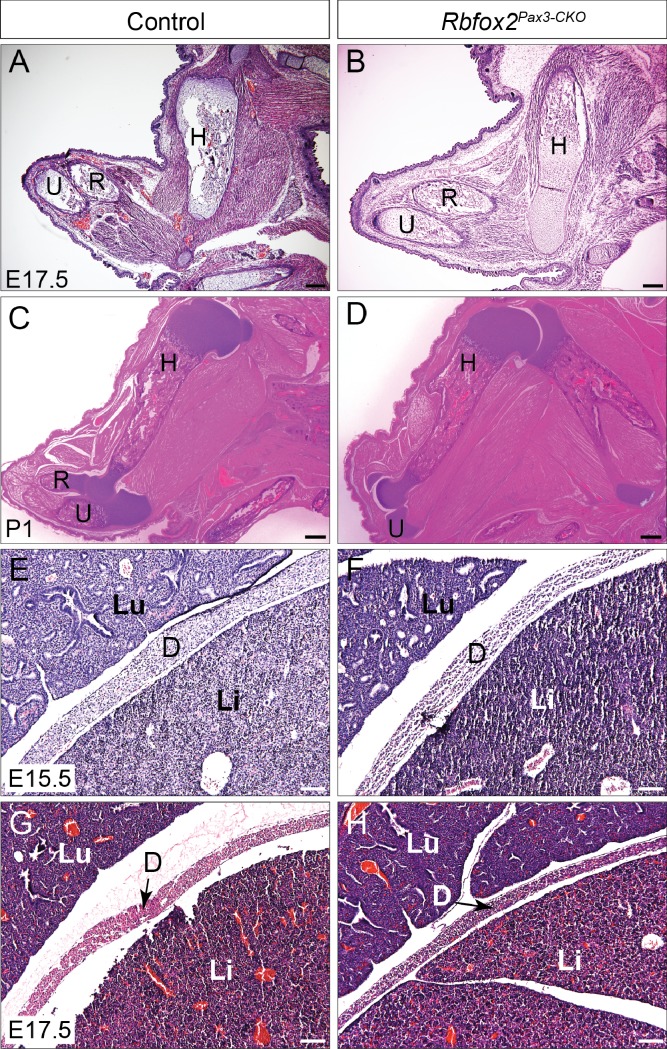
Figure 4. Craniofacial skeleton defects in Rbfox2 mutant embryos.
Alizarin red and Alcian blue stainings for ossified and chondrified tissues, respectively, of control (A–B), (D–E), (G), and I–J) and Rbfox2Pax3-CKO (C), (F), (H), and (K) skeleton at E17.5 (n = 8 controls, n = 6 Rbfox2Pax3-CKO). Alizarin red and Alcian blue stainings of control (L), (N), (P), and (R) and Rbfox2Wnt1-CKO (M, O, Q and S) skeleton at E18.5 (n = 8 controls, n = 5 Rbfox2Wnt1-CKO). Neural crest and mesoderm contribution to craniofacial bones are represented in green and pink color respectively (A, D and I). Dorsal (A–C and L–M), lateral (D–F and N–O) and ventral (I–K and R–S) view of skulls. Both Rbfox2Pax3-CKO (C), (F), (H), and K) and Rbfox2Wnt1-CKO (M), (O), (Q), and S) embryos demonstrate severe hypoplasia and diminished ossification of many neural crest-derived bones. Asterisks (*) represent the missing PPPL bone in Rbfox2 mutant embryos (K and S). AS, alisphenoid; BO, basioccipital; BS, basisphenoid; EO, exoccipital; F, frontal bone; IP, interparietal; MD, mandible; MX, maxilla; N, nasal; NC, nasal capsule; P, parietal bone; PL, palatine; PMX, premaxilla; PPMX, palatal process of maxilla; PPPL, palatal process of palatine; PPPMX, palatal process of premaxilla; PT, petrous part of temporal bone; SO, supraoccipital; SQ, squamous.