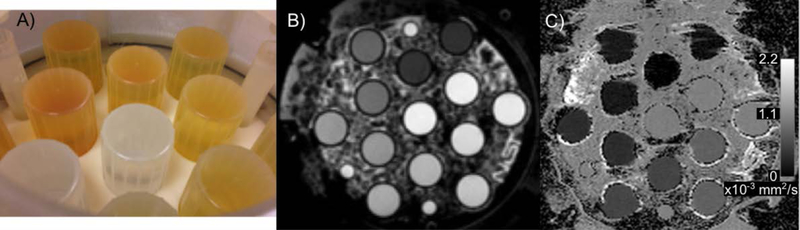
Figure 3:
NIST developed an isotropic diffusion phantom with support from NIH and RSNA-QIBA® based on the work of Pierpaoli et al. to identify an appropriate polymer, PVP, (22,23) and the ice-water phantom of Chenevert et al (31,32). A photo from the inside of the prototype diffusion phantom (A), a spin-echo image of the phantom filled with the ice water bath (B), and an apparent diffusion coefficient map with values in the phantom from approximately 0.2 to 1.1 × 10−3 mm2/s (C).