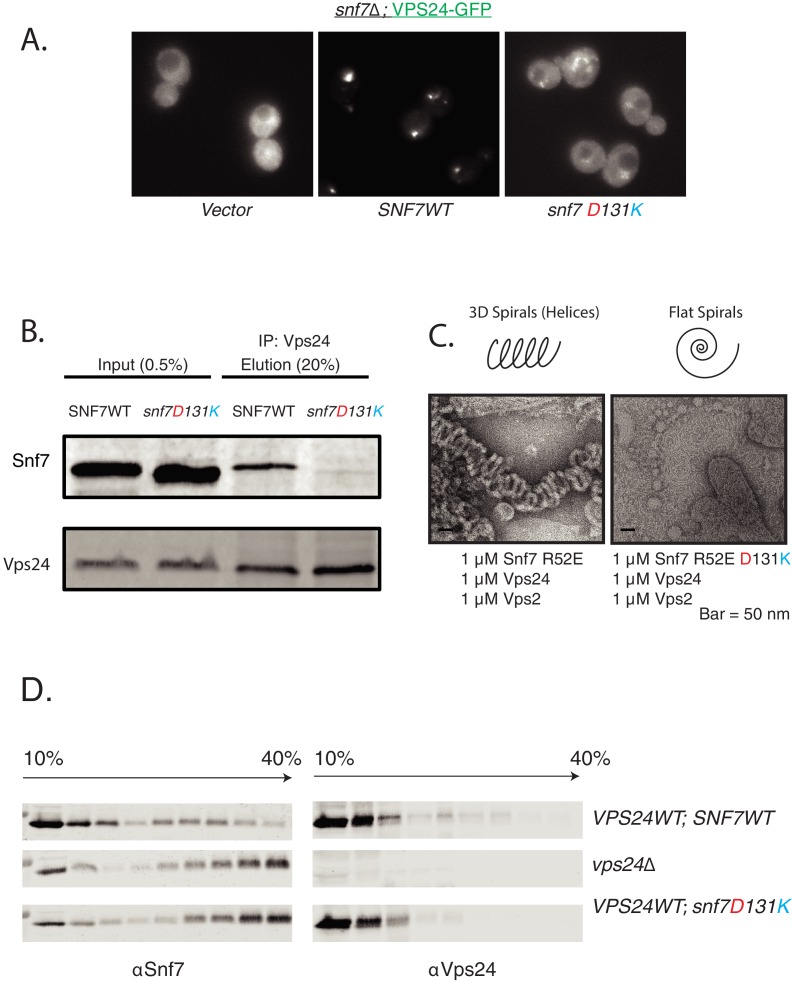
Figure 2. Helix-4 region of Snf7 is involved in recruiting Vps24.
(A) Helix-4 mutants fail to recruit Vps24-GFP. Vps24-GFP is present in endosomal dots in cells expressing SNF7 WT on a plasmid in a snf7Δ;Vps24-GFP strain, while with the mutation on Snf7, Vps24-GFP is more diffuse in the cytoplasm. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments, immunoprecipitating Vps24 and blotting for either wild-type Snf7 or the mutant D131K. (C) Electron microscopy assay on lipid monolayers, depicting co-assembly of Snf7 R52E with Vps24 and Vps2 into helices. Snf7 R52E D131K fails to form similar structures. Experiments were done with 1 μM of each protein incubated for 1 hr on lipid monolayers. (D) ‘In vivo’ glycerol-gradient experiments using a gradient of 10% to 40%, using various mutant strains annotated on the far-right. Western-blots were performed against Snf7 (left) or Vps24 (right).