Fig. (3).
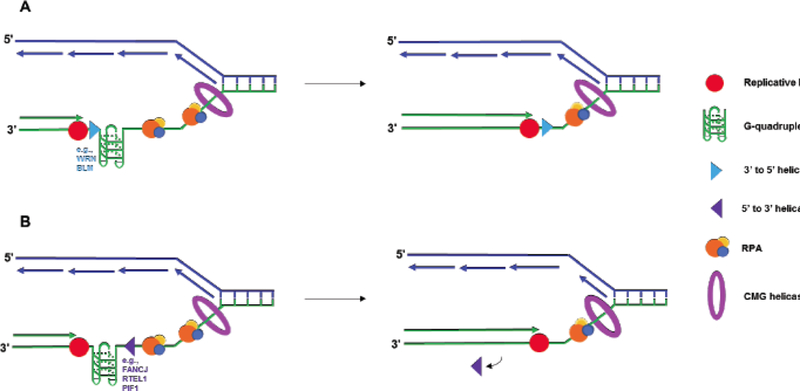
Coordinated action of DNA replication proteins during synthesis past G4 obstacle. A) A G-quadruplex DNA structure impedes leading strand synthesis during replication. As the CMG complex unwinds duplex DNA at the replication fork, RPA binds to stabilize the exposed single-stranded DNA. A 3′ to 5′ helicase, such as WRN or BLM, helps smooth over the G4 site, allowing the polymerase to synthesize the complementary strand. RPA heterotrimer is represented by spheres of orange (RPA70), blue (RPA32), and yellow (RPA14). B) Leading strand replication is again stalled by a G-quadruplex. The action of a 5’ to 3’ helicase, such as FANCJ, RTEL1, or PIF1, helps smooth the G-quadruplex in the direction opposite synthesis, resolving the replication block. The helicase dissociates from the DNA to allows the polymerase to proceed as synthesis continues.
