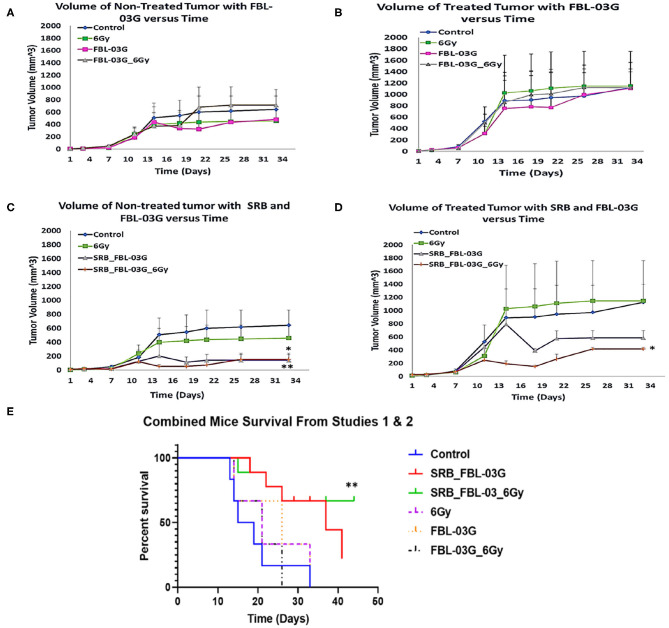
Figure 4.
In-vivo treatment of C57BL/6 mice. Mice were inoculated with 50 μL of KPC cells in PBS suspension at concentrations of 5 × 104 pancreatic cancer cells, on each left and right flank of mouse using a 22-Gauge syringe. When right side tumors reached palpable size, mice were randomized and treatments were administered. Mice were observed at least twice per week and tumor measurements were performed using precision calipers at least once per week. The abscopal effect was examined by monitoring the non-treated tumor. Smart radiotherapy biomaterials (SRB) loaded with FBL-03G (100 μg) significantly boosts the abscopal effect in pancreatic cancer slowing down tumor growth for both treated and untreated tumors. Two experiments were conducted simultaneously: Study 1 results are shown in graphs (A–D) and combined survival results for study 1 and study 2 results are displayed in (E). (A) Volumes of non-treated tumors over time without SRB (n = 3 for each cohort). (B) Volumes of treated tumors over time (n = 3 for each cohort). (C) Volume of non-treated tumors over time with SRB and FBL-03G (n = 3 for control and 6Gy cohorts respectively; n = 4 for SRB loaded with FBL-03G with/without radiotherapy cohorts respectively). (D) Volume of treated tumors over time for cohorts treated with SRB and FBL-03G (n = 3 for control and 6 Gy cohorts respectively; n = 4 for SRB loaded with FBL-03G with/without radiotherapy cohorts respectively). (E) Survival results show significant increase in survival for cohorts treated with SRB loaded with FBL-03G (each n = 9) compared to control (n = 6), 6Gy/FBL-03G/FBL-03G_6Gy (each n = 3). For Statistical Analyses (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) Student's T-Test was used for comparing the volumes of tumors for each treatment group versus those of the control group with no additional corrections, and Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) was used for the survival graphs.