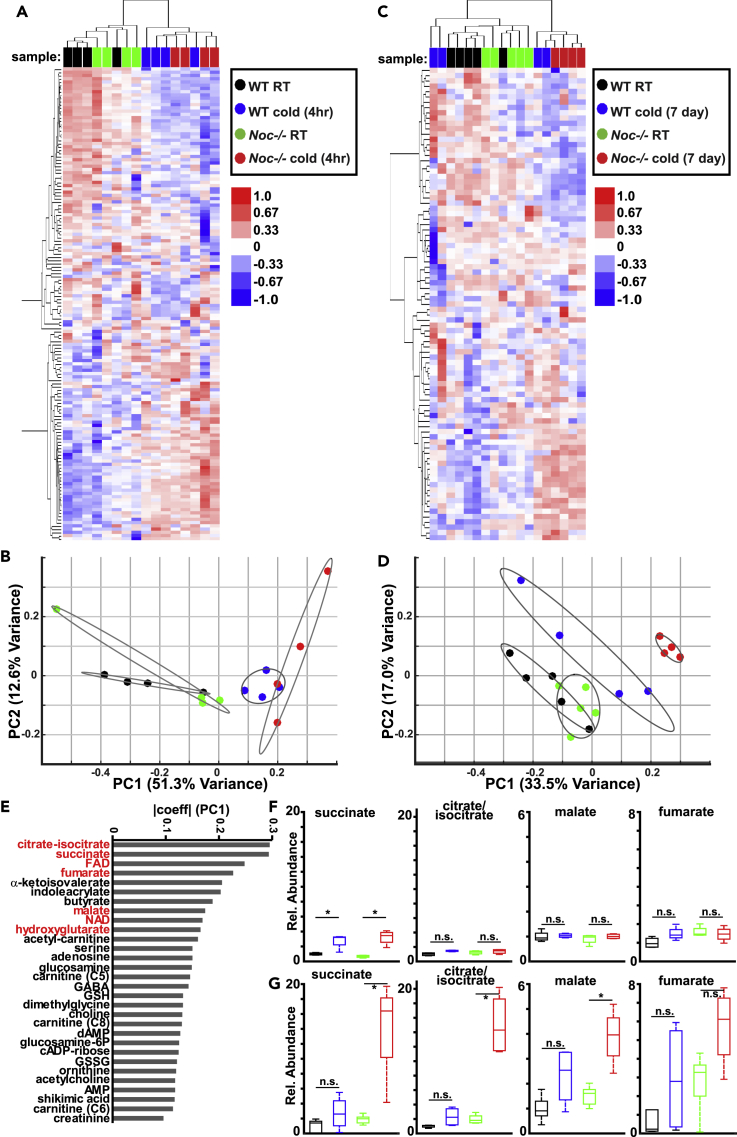
Figure 4.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Intermediates Are Altered in Nocturnin−/− BAT in Response to Prolonged Cold Exposure
(A) Heatmap representing hierarchical clustering of normalized metabolite abundances from the indicated genotypes, subject to room temperature (RT) or a 4-h cold exposure. Color bar reflects log-transformed abundance levels. Sample identity is indicated at the top of each column.
(B) Principal-component analysis of wild-type and Nocturnin−/− BAT subject to RT or a 4-h cold exposure. Ovals represent 95% confidence intervals. Contribution of each principal component to total variance is indicated. Same color scheme as (A).
(C) Heatmap representing hierarchical clustering of normalized metabolite abundances from the indicated genotypes, subject to RT or a 7-day cold exposure. Color bar reflects log-transformed abundances. Sample identity is indicated at the top of each column.
(D) Principal-component analysis of wild-type and Nocturnin−/− BAT subject to RT or a 7-day cold exposure. Same color scheme as (C). Ovals represent 95% confidence intervals. Contribution of each principal component to total variance is indicated.
(E) Contribution of the top 30 metabolites contributing to principal component 1 (PC1) for the principal component analysis of 7-day metabolomics shown in (D). Mitochondrial TCA-related metabolites are shown in red. Absolute magnitude of coefficients for each metabolite for PC1 (7-day) are plotted.
(F) Normalized abundances for select TCA metabolites in wild-type and Nocturnin−/− BAT subject to RT or a 4-h cold exposure. Boxplots display the median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and the range for metabolite levels. Same color scheme as (A). N = 4/genotype. *p < 0.05, as analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Tukey's post-hoc test; n.s., not significant.
(G) Same as (F), but for BAT subject to RT or a 7-day cold exposure. Same color scheme as (B). N = 4–5/genotype.
*p < 0.05, as analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Tukey's post-hoc test.
See also Figures S2 and S3 and Table S3.