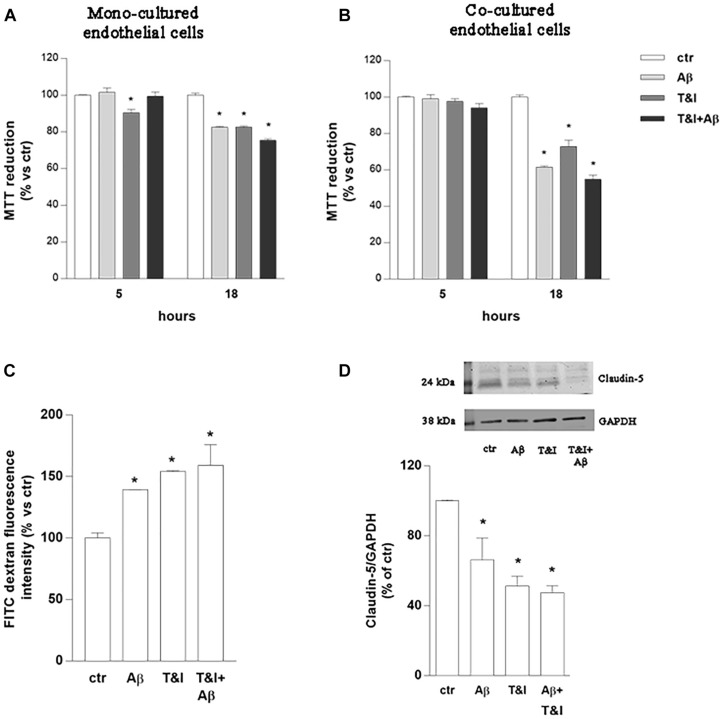
FIGURE 1.
Endothelial permeability is affected by Aβ under resting and inflammatory conditions. Endothelial mono-cultures (A) and co-cultures (B) were exposed to Aβ 1–42 (Aβ, 2.5 μM), TNFα+IFNγ (10 U/ml and 5 U/ml respectively, T&I) or their combination (Aβ+T&I). MTT assay was used to evaluate endothelial viability after different time points (5 and 18 h). Barrier properties of endothelial-astrocytes co-cultures, exposed for 5 h to Aβ (2.5 μM), T&I (U/ml and 5 U/ml respectively) or their combination (Aβ+T&I), were examined by measuring FITC-conjugated dextran permeability through the monolayer, 30 min after addition of the dye (C), and the expression of Claudin-5 by western blot analysis (D). Data are expressed as percentage of control viability (A,B). Barrier permeability is expressed as percentage of control of FITC-dextran-10 kDa fluorescent intensity, plotted on the Y-axis (C). Data are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments, each run in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control. Significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls test.