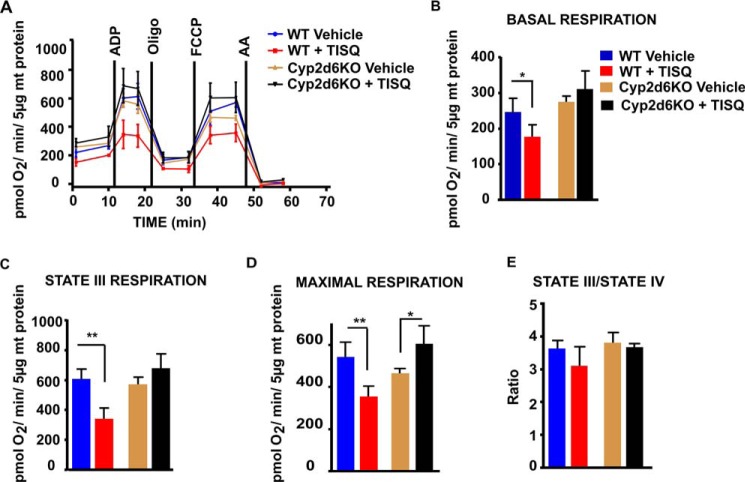
Figure 2.
In vivo effects of TISQ on brain mitochondrial respiratory controls. WT (n = 6) and Cyp2d6KO (n = 6) mice were injected intraperitoneally with TISQ (64 mg/kg b.w., n = 3) or vehicle (n = 3) for 21 days. Mitochondria freshly isolated from the brains were then used to measure OCRs in the Seahorse flux analyzer as described under “Experimental procedures.” A, respiratory profiles of brain mitochondria from vehicle-treated WT mice (WT Vehicle), TISQ-treated WT mice (WT + TISQ), vehicle-treated Cyp2d6KO mice (Cy2d6KO Vehicle), and TISQ-treated Cyp2d6KO mice (Cyp2d6KO + TISQ) are shown. B–E, basal respiration (B), state III (ADP-linked coupled) respiration (C), maximal respiration (D), and state III/IV respiration (E) using isolated brain mitochondria. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus vehicle. All values are represented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. n represents the number of mice used in each group.