Figure 2.
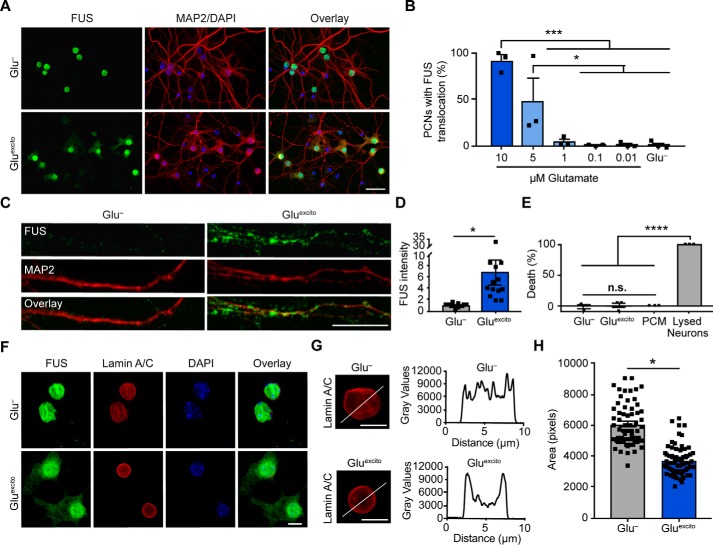
Cell viability and nuclear membrane integrity are intact under conditions of Gluexcito that promote FUS translocation. A, following excitotoxic insult, FUS egress and cytoskeletal rearrangements were detected by anti-FUS (green) and anti-MAP2 (red) staining, respectively. Scale bar = 40 μm. B and C, quantification of FUS translocation revealed a dose-dependent response to glutamate in neurons using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test (10 μm compared with 1 μm, ***, p = 0.0002; compared with 0.1 μm, ***, p = 0.0001; compared with 0.01 μm, ***, p = 0.0002; and compared with Glu−, ***, p = 0.0002; 5 μm compared with 0.1 μm, *, p = 0.0404; compared with 0.01 μm, *, p = 0.0426; and compared with Glu−, *, p = 0.0451; n = 3 biological replicates). C, increased dendritic FUS staining (green) was observed by confocal microscopy following excitotoxic stress. Dendrites were labeled with anti-MAP2 (red). Scale bar = 10 μm. D, quantification of C. Black squares represent the intensity of dendritic FUS staining per cell. Means represent the average of n = 4 biological replicates (Student's t test; *, p = 0.0142) normalized to the control (Glu−). E, cytotoxicity induced by Gluexcito was assessed after the washout period (Fig. 1A) with the LDH assay. In contrast to the positive control (neurons treated with lysis buffer; lysed neurons), membrane permeabilization was not detected for neurons exposed to Gluexcito. Neurons cultured in the absence of Gluexcito (Glu−) served as a negative control. Wells containing only primary neuron–cultured medium (PCM) served as a background control. Results reflect n = 3 biological replicates analyzed with a one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test (for all statistical comparisons, ****, p < 0.0001, n.s. = nonsignificant). F, immunofluorescence with anti-lamin A/C staining (red) and confocal microscopy revealed the nuclear envelope was thickened yet still intact within neurons exhibiting translocated FUS (green) after Gluexcito exposure. The time point is the same as E. Scale bar = 25 μm. G, representative line scan analyses of lamin staining demonstrates enhanced lamin intensity at the nuclear periphery in neurons exposed to excitotoxic insult (scale bars = 10 μm). B, D, E, and H, error bars represent S.E. H, quantification of nuclear size using the nuclear counterstain, DAPI, revealed a significant decrease in nuclear area following excitotoxic insult. Black squares represent the area of individual neurons. Means represent the average of n = 4 biological replicates (Student's t test; *, p = 0.0154).