Figure 1.
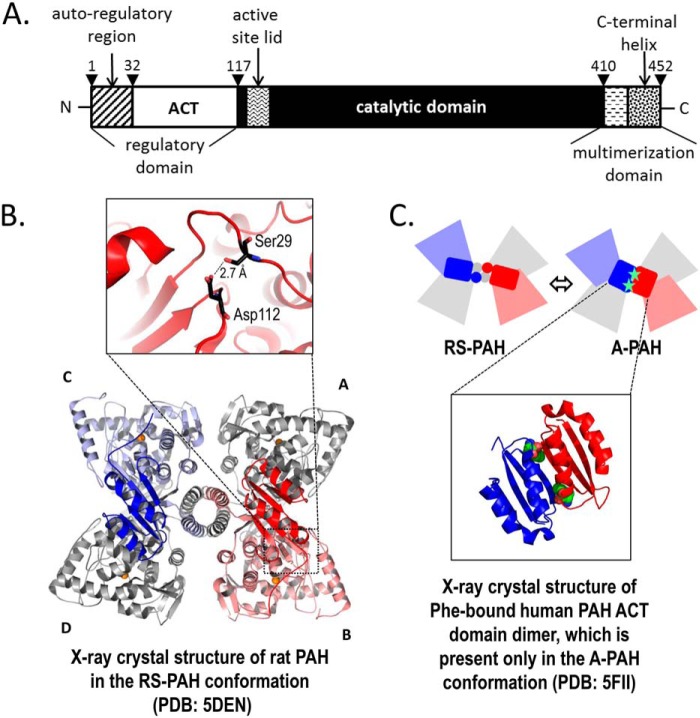
PAH structure. A, refined description of the domain structure of hPAH. The N-terminal 32 amino acids have been called an autoregulatory sequence, which together with the ACT subdomain (residues 33–110) constitute the regulatory domain (residues 1 to ∼117). The N-terminal ∼20 amino acids are disordered in all PAH crystal structures; residues 111–117 constitute a loop that connects the ACT subdomain to the rest of the protein. The residues between 118 and ∼410 have been defined as the catalytic domain. The region between 118 and 127 contains a tryptophan, whose intrinsic fluorescence changes upon enzyme activation (43), residues 128–148 constitute the active-site lid, and residues 137–141 are disordered in all full-length PAH structures in the RS-PAH conformation. Residues 411–453 have been designated as the multimerization domain based on truncation analysis. However, the crystal structure suggests that the β-hairpin at 411–424 might best be considered part of the catalytic domain. Residues 425 and 426 constitute a connection between this expanded catalytic domain and a long C-terminal α-helix (residues 427–452). The C-terminal helices form a 4-helix bundle that secures the tetramer (see B). The most C-terminal residues are disordered in all full-length mammalian PAH structures. B, illustrated is the highest-resolution structure of full-length rPAH in the RS-PAH conformation (7). The regulatory domains of subunit B (red) and subunit C (blue) are in bolder tones. Subunits A and D are colored gray. The interaction between the auto-regulatory region and the catalytic domain, which partially occludes the active site in the RS-PAH conformation, is stabilized by a 2.7 Å hydrogen bond between Ser-29 and Asp-112 (inset). C, top is a schematic of the RS-PAH ⇔ A-PAH conformational interchange using coloring as in B. Bottom is the crystal structure of the ACT-domain dimer of hPAH with allosteric Phe bound (shown as spheres) (6). The repositioned regulatory domain in the A-PAH conformation releases active-site occlusion (not shown).