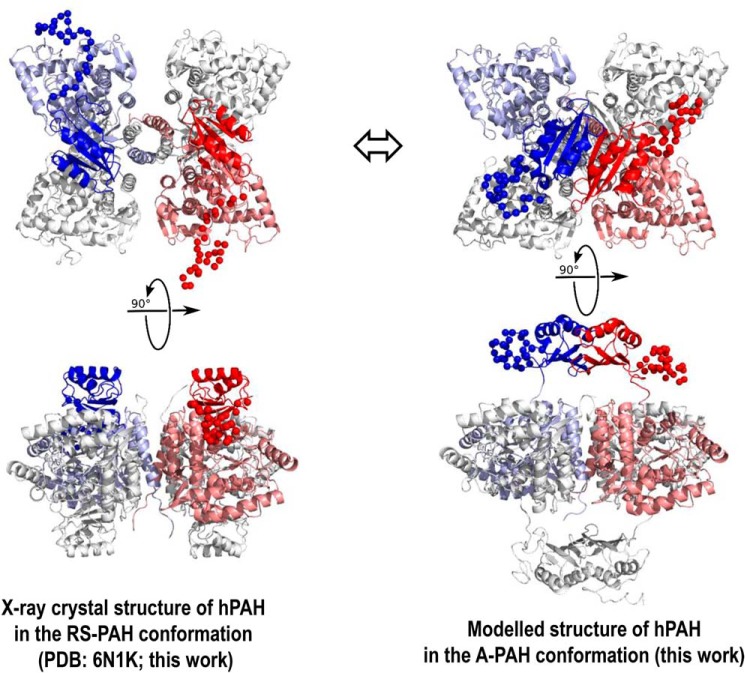
Figure 6.
Structures of human PAH. A, X-ray crystal structure of hPAH in the RS-PAH conformation is illustrated (PDB code 6N1K). As in Fig. 1, the regulatory domains of subunit B (red) and subunit C (blue) are in bolder tones. Subunits A and D are colored gray. The disordered regions (missing inventory) are shown as balls and were modeled using NAMD to reconcile the crystal structure with the solution structure obtained from SAXS analysis. B, model of the A-PAH conformation, which contains a repositioned regulatory domain that no longer occludes the active site and contains an ACT-domain dimer. This model, the optimization of which is extensively discussed herein, employs the crystal structure of the truncated ACT domain of human PAH (residues 34–111) with allosteric Phe bound (PDB code 5FII (6)). The illustrated conformation of the entire autoregulatory region is shown as balls, as modeled by NAMD. The best-fit model contains the ACT-domain dimers at 8–10 Å farther from the tetramer center of mass than had previously been considered (see Fig. 7).