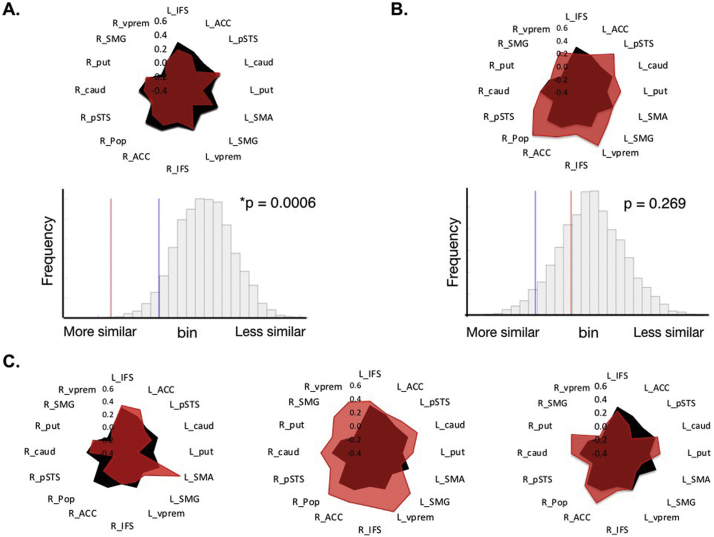
Fig. 3.
Individual variation in patient connectivity fingerprints. Comparing the functional connectivity fingerprint of individual patients to the template fingerprint of controls identified a statistical match in some patients (A), but not in others (B). In both cases, the fingerprint of the individual patient (red) is overlaid onto the average fingerprint of all controls (black) and shown alongside the result of statistical permutation tests. In patient A, the difference between the patient's fingerprint and that of the healthy controls (observed test statistic, red line) is smaller than expected by chance (criterion value, blue line), indicating a statistical match between the two fingerprints (permutation p-value = 0.0006). In patient B, the difference did not pass the criterion value, i.e. this patient's fingerprint was not a match to controls (p = 0.27). C. Three individual patients whose fingerprints statistically deviated from ‘normal’ in unique ways, including globally increased functional connectivity or heightened connectivity to specific brain structures. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)