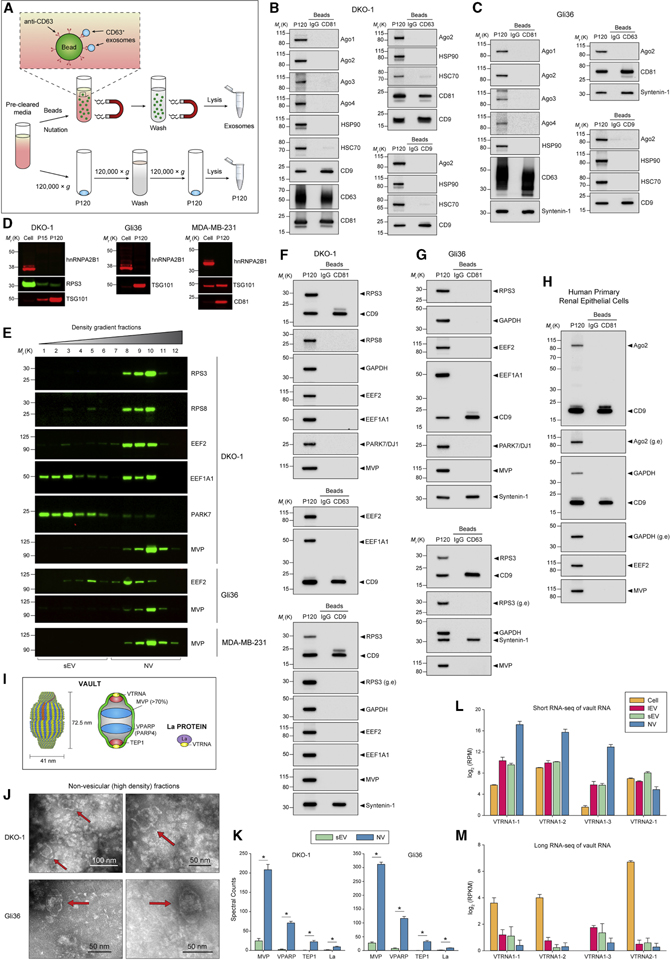
Figure 4. Extracellular Release of RNA-Binding Protein and Vaults.
(A) Schematic illustration of the direct immunoaffinity capture (DIC) procedure. Magnetic beads directly conjugated to anti-CD63, anti-CD81, anti-CD9 antibodies or IgG were added directly to pre-cleared cell culture medium (STAR Methods) without prior ultracentrifugation or concentration. In parallel, conventional crude sEVs (P120) were prepared form the same pre-cleared cell culture medium.
(B-C) DIC of CD81-, CD63-and CD9-positive exosomes from (B) DKO-1 or (C) Gli36. Immunoblots of crude sEV pellet (P120) and bead-captured exosomes.
(D) Immunoblots of whole cell lysates, large EVs (P15) and crude small EVs (P120) obtained by ultracentrifugation.
(E) Immunoblots of high-resolution density gradient fractionation of crude small EVs (P120).
(F-H) DIC of CD81-, CD63-and CD9-positive exosomes. Immunoblot of crude sEV pellet (P120) and bead-captured exosomes from (F) DKO-1, (G) Gli36, and (H) cultured primary human renal epithelial cells. g.e, greater exposure.
(I) Structure and molecular composition of vaults.
(J) Non-fixed negative stain TEM of DKO-1 and Gli36 NV fractions. Red arrows indicate vault structures.
(K) Proteomic analysis of vault-associated proteins in purified sEV and NV generated by gradient density centrifugation. Data are mean ± SD. *p < 0.00001 for the quasiFDR.
(L) Short RNA-seq data for vault RNA in DKO-1 cells, large EVs (lEV), sEV and NV pooled fractions. RPM, reads per million.
(M) Long RNA-seq data for vault RNA in DKO-1 cells, large EVs (lEV), purified sEV and non-vesicular (NV) pooled fractions. FPKM, fragments per kilobase million.
See also Figure S4.