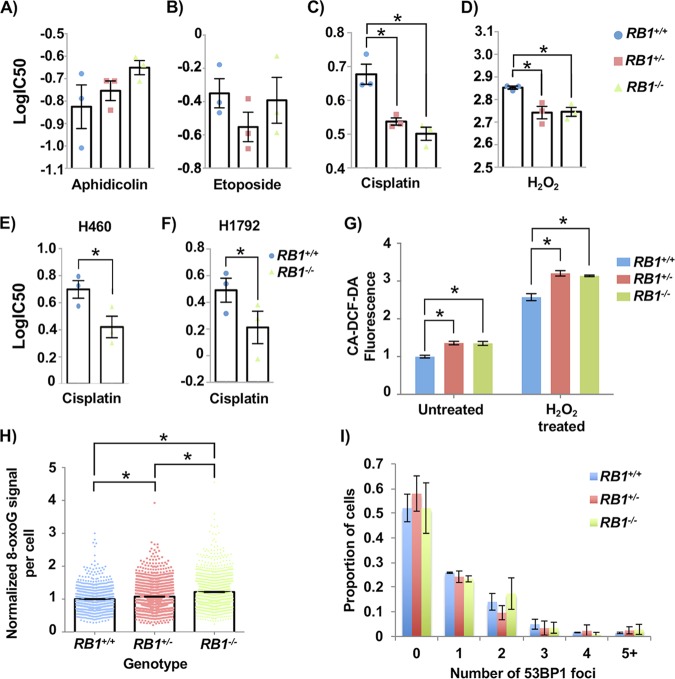
FIG 2.
Cancer cells with RB1 mutations have elevated reactive oxygen species levels and sensitivity to cisplatin. (A to D) Aphidicolin (A), etoposide (B), cisplatin (C), and hydrogen peroxide (D) were added to cultures of the indicated genotypes of U2OS cells. Viability was assessed after 72 h using alamarBlue, and dose-response curves were used to calculate IC50 values for each genotype. Both RB1 mutant genotypes have significantly lower IC50 values in response to cisplatin and hydrogen peroxide than control U2OS cells (as determined by one-way ANOVA). (E and F) H460 and H1792 cancer cells with RB1 mutations were treated with cisplatin as described above for panel C. Differences in IC50 values were determined using a paired t test. (G) To detect ROS, CA-DCF-DA was added to culture medium at the end of 72 h of mock or hydrogen peroxide treatment. Normalized fluorescence was averaged for four clones of RB1 wild-type and knockout genotypes and for three clones for the heterozygous genotype. Mean values were compared by two-way ANOVA. (H) Cells were fixed and stained for 8-oxoG and DAPI and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The average 8-oxoG signal per nucleus was determined using ImageJ, with DAPI staining defining the nuclear area. Three clones per genotype were used, and data were normalized to the mean signal from RB1 wild-type cells in duplicate experiments. Statistical significance in staining intensity was determined by Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance and Dunn’s multiple-comparison test. (I) 53BP1 foci were quantitated for each RB1 genotype using Focinator as with γH2AX. No significant differences were observed, as determined by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. At least 120 cells from one U2OS clone were analyzed in duplicate experiments for each RB1 genotype. All error bars are ±1 SEM. *, P < 0.05.