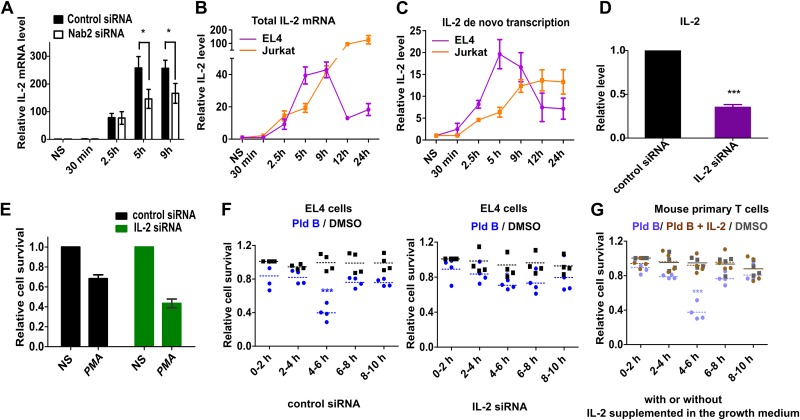
FIG 4.
IL-2 mediates the sensitivity to splicing inhibition sensitivity. (A) Relative IL-2 expression in the presence and absence of Nab2 (mean ± SD; n = 3); (B) temporal IL-2 total mRNA level in EL4 and Jurkat cells (mean ± SD; n = 3); (C) IL-2 de novo transcription dynamics in EL4 and Jurkat cells (mean ± SD; n = 3); (D) siRNA knockdown efficiency for IL-2 in EL4 cells (mean ± SD; n = 3); (E) cell viability analysis in IL-2 knockdown EL4 cells at 48 h poststimulation (relative to that in nonstimulated cells) (mean ± SD; n = 3); (F) temporal splicing modulation analysis (with Pld B) in siRNA-transfected EL4 cells; (G) temporal splicing modulation analysis in mouse primary T cells in the presence of growth medium supplemented or not supplemented with IL-2. We used the data from the assay whose results are presented in Fig. 1C for direct comparison of conditions with or without IL-2 supplementation. Experiments were performed in parallel. *, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001 (Student's unpaired t test, done using GraphPad software).