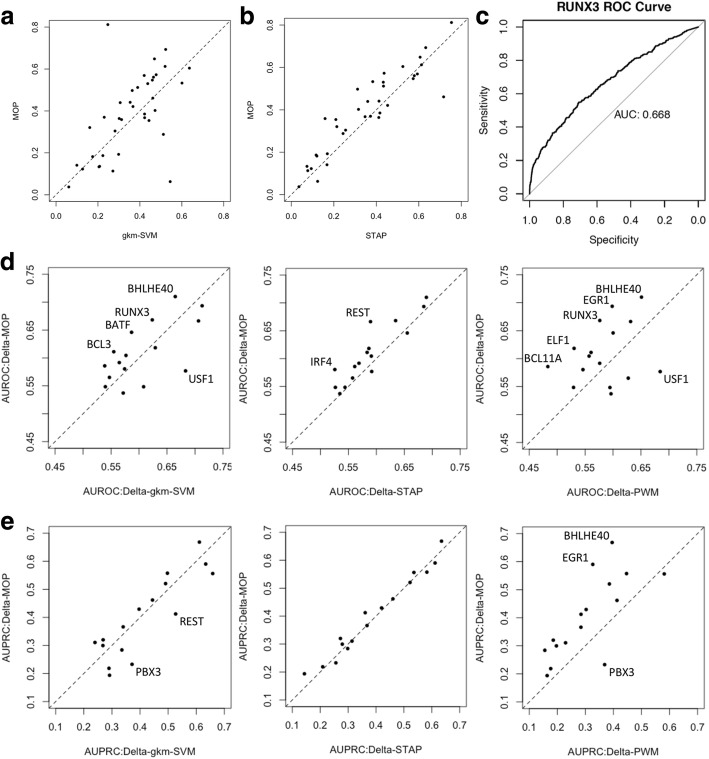
Fig. 2.
a, b Comparison of three TF binding predictors. We compared MOP with STAP and gkm-SVM. The performance of each model is measure by the Pearson correlation coefficient (CC) between ChIP score and predicted binding score on a test set of 400 sequences that are not used in model training. Performance evaluation is performed for each of 37 data sets (for different TFs). a MOP performs as well or better than STAP (using the best motif when multiple motifs are available) for 26 of the 37 data sets, with their average CC being 0.39 and 0.36 respectively. b MOP performs as well or better than gkm-SVM for 21 of 37 TF data sets examined, with average CC of the two methods being 0.39 and 0.37 respectively. c–e Evaluation of TFBS-SNP impact prediction methods. Four different methods of binding change prediction (Delta-MOP, Delta-gkm-SVM, Delta-STAP, and Delta-PWM) were evaluated for their ability to predict allele-specific binding (ASB) events from non-ASB events, for each of 16 data sets based on ChIP-seq data for different TFs. Performance was measured using AUROC as well as AUPRC. ROC curve of RUNX3 using “Delta-MOP” as impact predictor is shown in (c). The last two rows show pairwise comparison of Delta-MOP and each of the other three methods based on AUROC (d) and AUPRC (e) achieved by the methods on the same data set