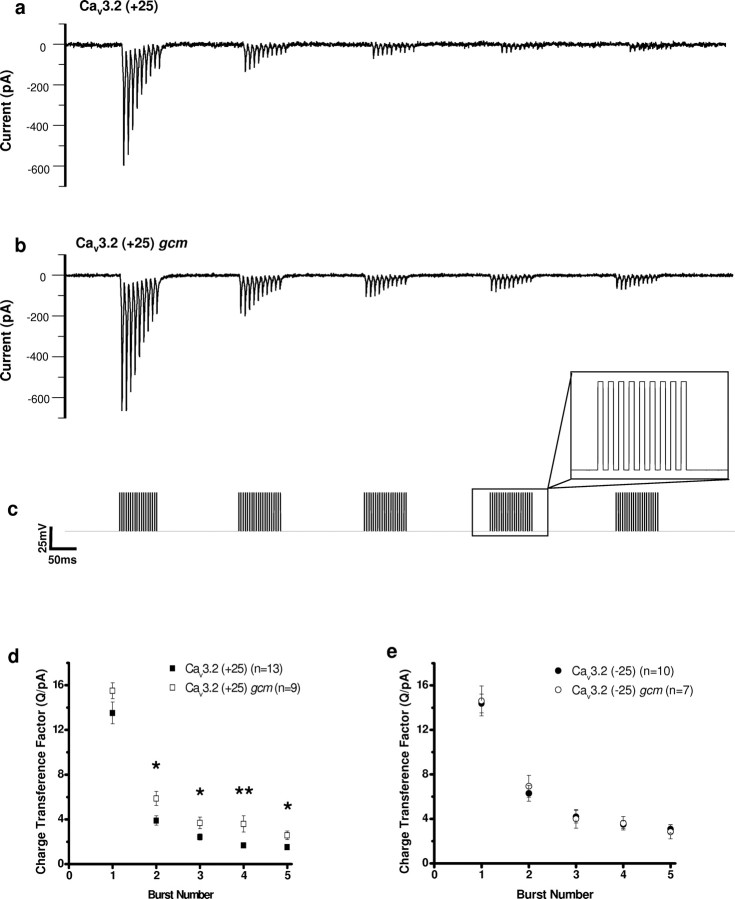
Figure 5.
The gcm increases the charge transference of Cav3.2 (+25) during high-frequency burst depolarizing trains. a–c, Representative traces of Cav3.2 (+25) wild-type (a) and Cav3.2 (+25) gcm (b) currents recorded during high-frequency depolarizing train pulses (125 Hz for 80 ms) from −70 to −20 mV occurring in bursts (5 Hz for 1 s) (c). Charge transference of Cav3.2 during each burst was divided by the peak current on first pulse of the first burst to account for variations in current magnitude. d, In Cav3.2 (+25), the gcm significantly increased the charge transference factor in all subsequent bursts after one 125 Hz burst. e, In Cav3.2 (−25), the gcm had no significant effect on the charge transference factor. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, significant difference between charge transference factors (ANOVA).