Figure 6.
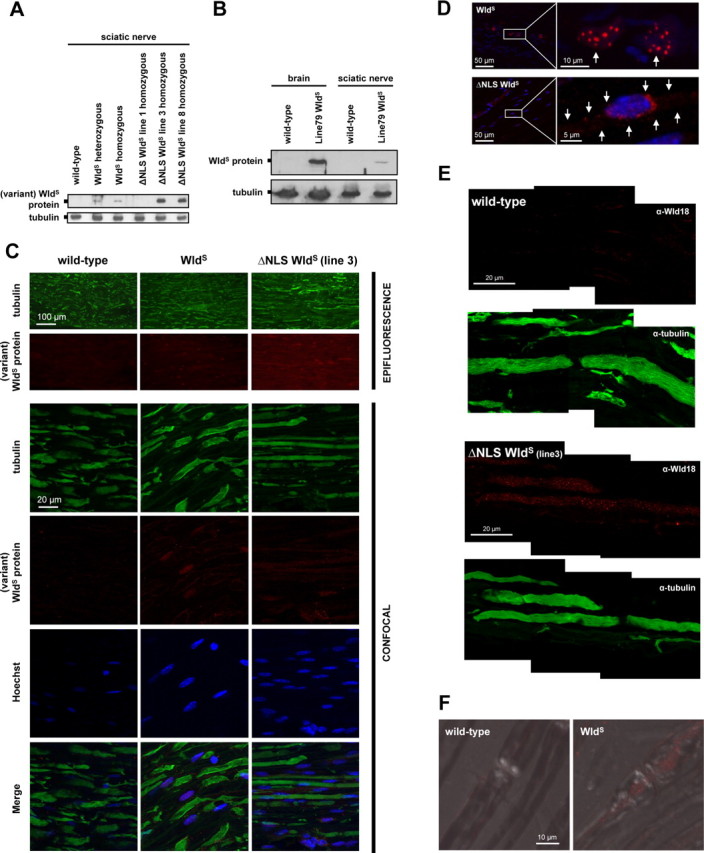
Detection of WldS and variant ΔNLS WldS proteins in nerves in vivo. A, Western blot showing presence of variant WldS proteins in sciatic nerve extracts from both spontaneous WldS mice and ΔNLS WldS transgenics. Note markedly higher levels of variant WldS protein in extracts from ΔNLS WldS lines 3 and 8 compared with WldS (heterozygous and homozygous). B, Western blot showing presence of WldS protein in sciatic nerve extracts from transgenic WldS rat (line 79, homozygous). For comparison, detection of WldS in similar total protein amount from brain homogenate from the same rat is also shown. C, Fluorescence immunostaining on wild-type, WldS (homozygous), and ΔNLS WldS (line 3, homozygous) longitudinal sciatic nerve sections using tubulin (green) and Wld18 (red) antibodies. Conventional epifluorescence microscopy (rows 1 and 2) demonstrates more intense Wld18 labeling in sciatic nerve from ΔNLS WldS mouse than from WldS. Higher-resolution confocal images (rows 3–6) from the same sections show variant WldS protein signals in glial cells whose nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). Note more prominent Wld18 staining in sample from ΔNLS WldS sciatic nerve. D, Confocal images showing induction of variant WldS expression (red) in glial cells 6 h after sciatic nerve injury located distally from the lesion site. Note nuclear WldS foci in activated glial cells (arrows, upper row) from native WldS mutant, whereas induced ΔNLS WldS protein expression shows a more cytoplasmic staining pattern demarcating the cell body (arrows, lower row). Blue, Hoechst 33258 counterstain. E, High-power confocal composite (z-series projection) shows presence and homogenous distribution of variant WldS protein (red) in the nodal and internodal axoplasm of ΔNLS WldS sciatic nerve (line 3) which is counterstained with tubulin (green). Note the fine granular staining pattern of Wld18 antibody within the axoplasm. Variant WldS protein immunoreactivity is absent from wild-type sciatic axons. F, Confocal images (z-series projection + DIC merge) showing localization of WldS protein (red) in nodal and perinodal axoplasm of native WldS axon in contrast to wild-type fiber where WldS signal is absent (Wld18 antibody plus Alexa568-tyramide signal amplification).
