Figure 2.
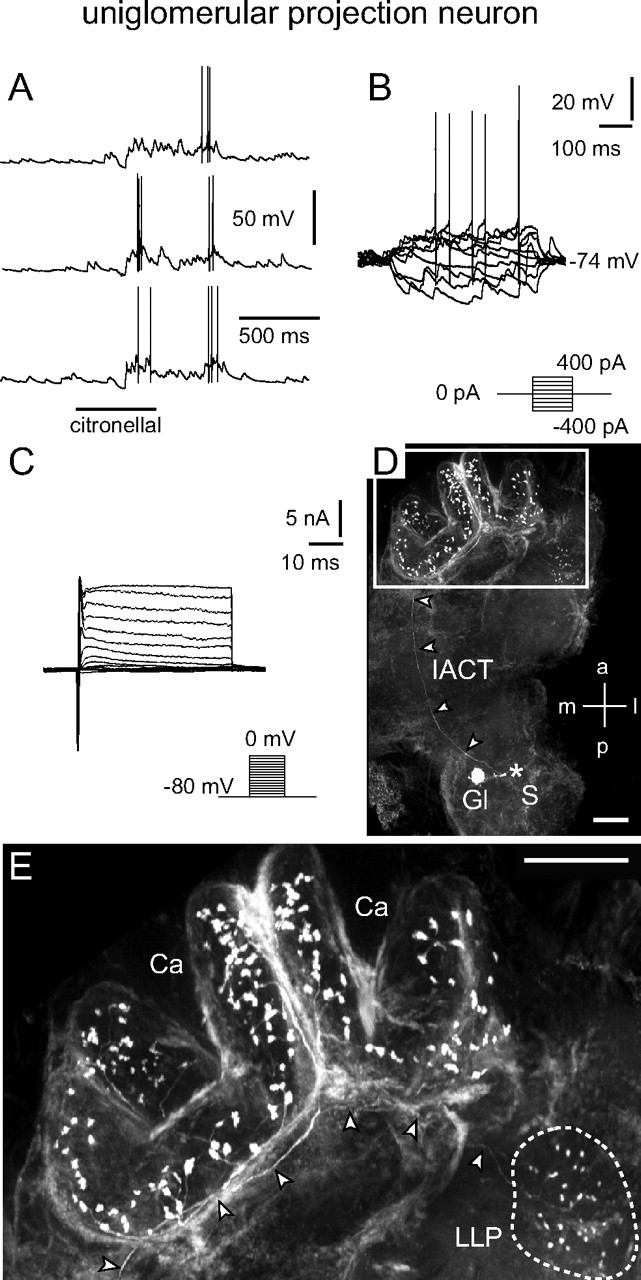
uPN: electrophysiological and morphological characteristics. A, B, Odor stimulation (A) and injection of depolarizing current (B) induced overshooting action potentials. Current was injected for 500 ms from −400 to 400 pA in 100 pA steps. C, Whole-cell recordings of (mainly) voltage-activated currents in normal saline. Depolarizing voltage steps from a holding potential of −80 mV elicited a fast transient inward current followed by transient and more sustained outward currents. Both the inward and outward currents consisted of several ionic currents in combination. By using ion substitution, standard pharmacological agents, and appropriate voltage protocols, several components of the inward and outward currents were identified. The transient, fast activating/inactivating inward current was a TTX-sensitive Na+ current. A smaller, more sustained inward Ca2+ current was masked by large outward currents. The outward currents consisted of at least three components: (1) a transient, 4-AP-sensitive, voltage-dependent current (IA); (2) a more sustained, TEA-sensitive, voltage-dependent current (IK(V)); and (3) a voltage- and Ca2+-dependent, TEA-sensitive outward current (IO(Ca)). D, E, Morphology of the recorded neuron revealed by staining via the patch pipette (360 μm image stack). D, The position of the soma (S), which was lost during processing, is marked (*). The neuron innervated a single glomerulus and sent a single axon along the IACT (arrowheads) to the mushroom body's calyces (Ca) and the lateral lobe of the protocerebrum (LLP). E, Higher magnification of the framed area from D showing boutons of the uPN in the calyces and an axon (arrowheads) that terminates in boutons innervating the LLP (outlined by dotted line). a, Anterior; Ca, calyces; Gl, glomerulus; l, lateral; LLP, lateral lobe of the protocerebrum; m, medial; p, posterior; S, soma. Scale bars: D, E, 100 μm.
