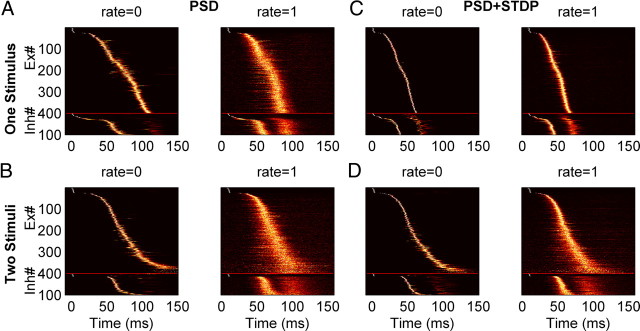
Figure 6.
Sensitivity to background spiking noise with different learning rules. A–D, Neurograms of the trajectories produced by training with one (A, C) and two stimuli (B, D) averaged over 200 posttraining trials. Each line represents the normalized PSTH of a single unit. Simulations were performed without spontaneous spiking activity (rate = 0) or with spontaneous spikes (1 Hz Poisson noise). Neurograms show the increased jitter in the presence of noise [performance: (A) p = 0.99 (left), p = 0.49 (right); (C) p = 0.6 (left), p = 0.57 (right); (B) p = 0.87 (left), p = 0.32 (right); (D) p = 0.92 (left), p = 0.45 (right)]. Compared with PSD, the neural trajectories of networks trained with PSD+STDP were more robust because they exhibited less jitter.