Figure 8.
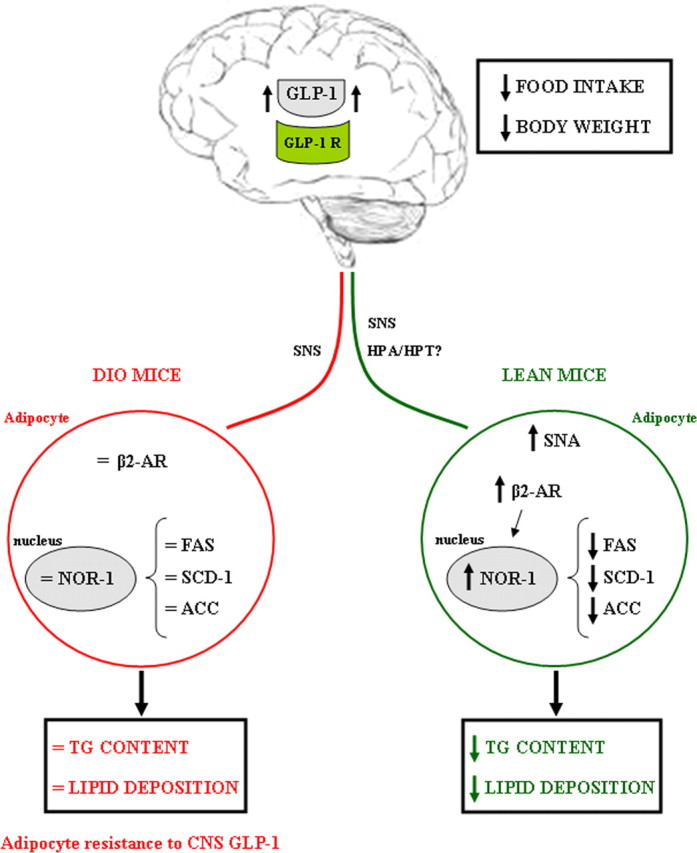
Schematic overview summarizing the pharmacological effects of CNS GLP-1 on fat tissue. Stimulation of CNS GLP-1 increases sympathetic nerve activity in lean mice, leading to a stimulation of β2-AR and NOR-1 and thereby decreasing the expression of some key enzymes promoting lipid deposition. The role of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis and/or the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis needs to be elucidated. These metabolic changes in fat tissue represent a synergistic shift in substrate choice and nutrient partitioning, resulting in decreased energy storage. Contrary, in DIO mice, CNS GLP-1 loses its capacity to act on WAT, indicating that obesity induces an adipocyte resistance to CNS GLP-1.
