Figure 4.
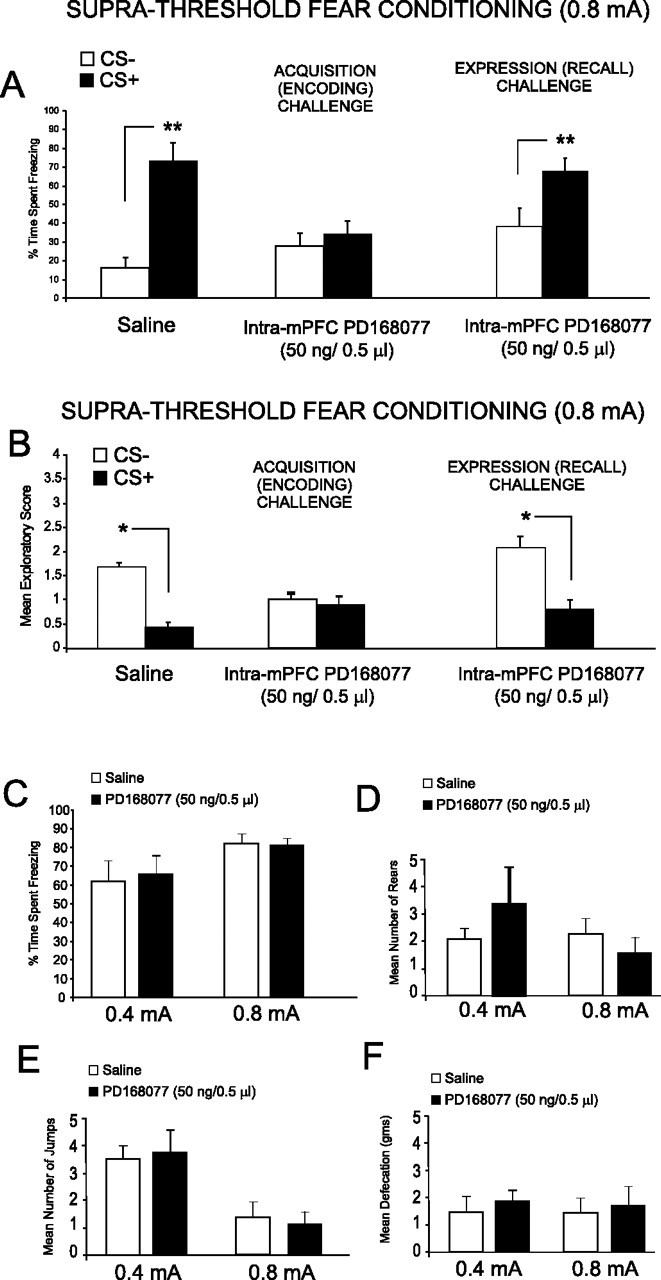
Intra-mPFC D4 agonist effects on suprathreshold olfactory fear conditioning and footshock sensitivity analyses. A, Saline control rats showed significant freezing behavior to CS+ versus CS− presentations after conditioning with suprathreshold footshock (0.8 mA) levels. In contrast, preconditioning microinfusion of intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/0.5 μl) blocked the acquisition of suprathreshold olfactory fear conditioning as demonstrated by no significant difference in the percentage of time spent freezing to the CS+ relative to the CS− at testing. However, intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/0.5 μl) microinfusions immediately before testing did not block the expression (recall) of suprathreshold olfactory fear conditioning. B, Analysis of exploratory activity after CS+ or CS− presentation revealed that whereas saline control rats showed significant conditioned suppression of exploratory behavior in response to CS+ versus CS− presentations, this effect was blocked in rats receiving intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/0.5 μl) immediately before conditioning. In contrast, intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/0.5 μl) administered immediately before testing did not block the expression (recall) of suprathreshold olfactory fear conditioning observed as a significant decrease in exploratory behavior in response to CS+ presentations. C, Footshock sensitivity testing (see Materials and Methods) revealed no significant differences between control groups receiving a subthreshold footshock (0.4 mA) versus intra-mPFC saline control (n = 5) or intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/μl; n = 5) or between control groups receiving a suprathreshold level of footshock (0.8 mA) versus intra-mPFC saline control (n = 6) or intra-mPFC PD 168077 (50 ng/μl, n = 6) in the percentage of time spent freezing in response to footshock presentations. D, Similarly, no significant differences were observed in the mean number of rears between groups in response to either level of footshock. E, No significant differences were observed between the mean numbers of jumps between groups in response to either level of footshock. F, No significant differences were observed in the mean amount of defecation between groups in response to either level of footshock.
