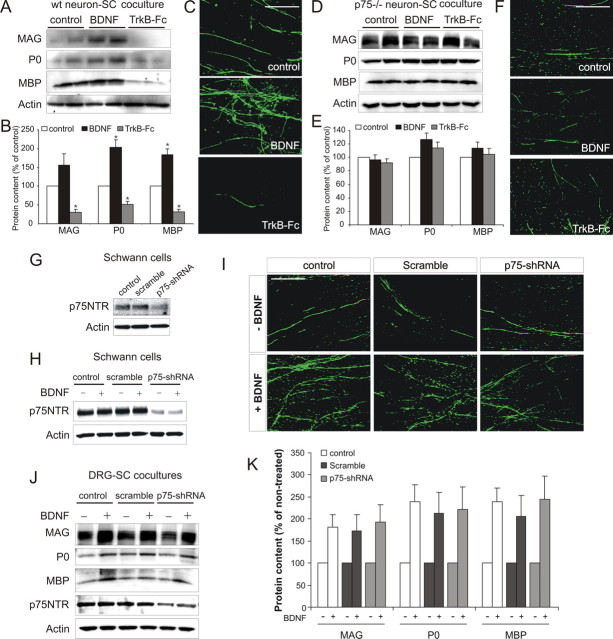
Figure 3.
BDNF activates neuronal p75NTR receptors to promote myelination. A, B, Western blot (A) including densitometric analysis (B; mean ± SEM, n = 3) of cocultures containing NGF-dependent neurons from wild-type mice. BDNF increased myelin protein expression, whereas TrkB–Fc inhibited it (*p < 0.01 vs control). C, MBP immunostaining of parallel cultures. Compared with controls, a qualitative increase in MBP+ myelin segments occurred with BDNF but was reduced with TrkB–Fc. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, E, Western blot (D) including densitometric analysis (E; mean ± SEM, n = 3) of cocultures containing NGF-dependent neurons from p75NTR−− mice. Neither BDNF nor TrkB–Fc altered myelin protein expression. F, MBP immunostaining of parallel p75NTR−− cultures. No qualitative change in MBP+ myelin segments was observed with either BDNF or TrkB–Fc. Scale bar, 100 μm. G–K, BDNF enhances myelination after p75NTR knockdown in Schwann cells. G, Western blot of noninfected (control), scrambled shRNA-infected, or p75NTR–shRNA-infected Schwann cell cultures. Knockdown of p75NTR expression was only observed in p75NTR–shRNA-infected cultures. H, BDNF had no effect on p75NTR expression in either control, scramble-infected, or p75NTR–shRNA-infected cultures. I–K, MBP immunostaining (I) and Western blot (J) including densitometric analysis (K; mean ± SEM, n = 3) of cocultures containing control, scramble-infected, or p75NTR–shRNA-infected Schwann cells. No qualitative change in MBP+ myelin segments or quantitative change of myelin protein expression occurred as a consequence of p75NTR knockdown. Scale bar, 100 μm.