Figure 7.
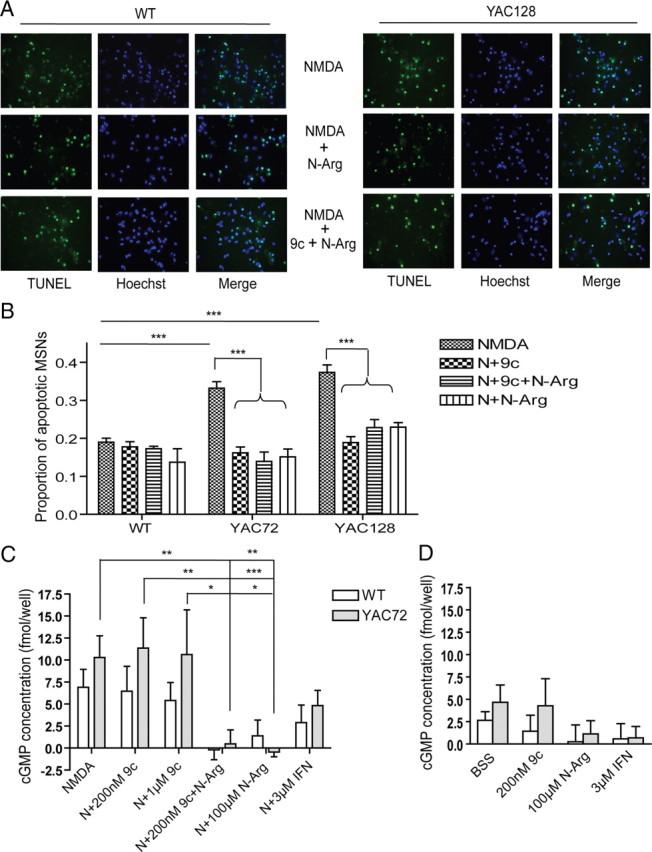
nNOS inhibitor (N-Arg) reduces NMDA-induced toxicity and occludes effect of Tat–NR2B9c in YAC72 and YAC128 but not WT cultured MSNs. A, Representative photomicrographs showing TUNEL- and Hoechst-stained WT and YAC128 MSNs pretreated with 100 μm N-Arg (middle) and 200 nm Tat–NR2B9c plus 100 μm N-Arg (bottom) for 1 h before 10 min exposure to NMDA. B, Average proportion of apoptotic MSNs after pretreatment with 100 μm N-Arg and/or 200 nm Tat–NR2B9c (9c) and exposure to 500 μm NMDA (N) showed a similar reduction in YAC72 and YAC128 MSNs and no significant reduction in WT MSNs (mean values calculated after subtraction of percentage apoptosis in NMDA-untreated condition for each experiment). Tested by two-way ANOVA, significant for both genotype and treatment, n = 6; F(1,42) = 48, p < 0.0001 for genotype; F(5,42) = 70, p < 0.0001 for treatment F(5,42) = 9, p < 0.0001 for interaction (***p < 0.001, by Bonferroni's post hoc tests). C, The 500 μm NMDA-induced cGMP production of WT and YAC72 MSNs after pretreatment with 100 μm N-Arg and/or 200 nm/1 μm Tat–NR2B9c or 3 μm IFN. Significance was tested by two-way ANOVA; n = 5 for WT and n = 6 for YAC72, significant for treatment. F(1,46) = 3, p > 0.05 for genotype; F(5,46) = 6, p < 0.0001 for treatment; F(5,46) = 0.7, p > 0.05 for interaction (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, by Bonferroni's post hoc tests). D, Basal cGMP production of WT and YAC72 MSNs after pretreatment with 100 μm N-Arg and/or 200 nm/1 μm Tat–NR2B9c, BSS, or 3 μm IFN. Significance tested by two-way ANOVA, n = 5 for WT and n = 6 for YAC72. F(1,33) = 1, p > 0.05 for genotype; F(3,33) = 1, p > 0.05 for treatment; F(3,33) = 0.2, p > 0.05 for interaction.
