Figure 1.
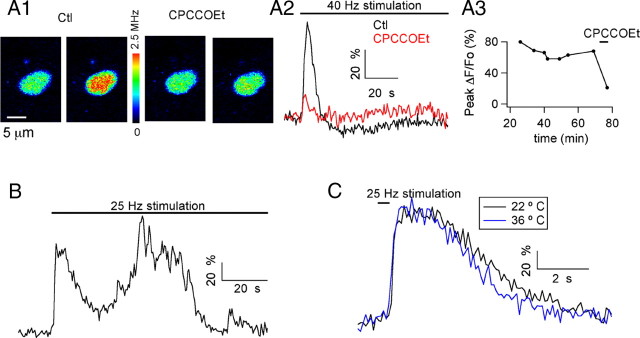
Stimulation of glutamatergic fibers induces mGluR1-dependent Ca2+ rises in MLI somata. A1, Pseudocolor images from a MLI soma preloaded with the Ca2+-dependent indicator OG1 taken at rest and at the peak of the response to a 1.5-min-long train of stimuli at 40 Hz. Images are shown in control solution (first and second images) and in the presence of a 100 μm concentration of the mGluR1 antagonist CPCCOEt (third and fourth images). A2, Time course for the ΔF/Fo signals. A3, Evolution of the peak ΔF/Fo values as a function of time in WCR before and during exposure to CPCCOEt. Experiment conducted at 22°C. B, In another preloaded MLI soma, extracellular stimulation (25 Hz, 1.6 min duration) evoked oscillatory changes in Ca2+. Experiment conducted at 36°C. C, Time course of the somatic Ca2+ signals elicited in another MLI by a 0.4 s train of 25 Hz stimuli at 22°C and 36°C. In this and subsequent figures, the pseudocolor bar for images from 2PLSM is expressed in Hz, calculated from the number of photons acquired during 10 μs sampling intervals. Note that in all experiments, ionotropic GABA and glutamate receptors were blocked by a mixture of antagonists, as specified in Materials and Methods.