Figure 3.
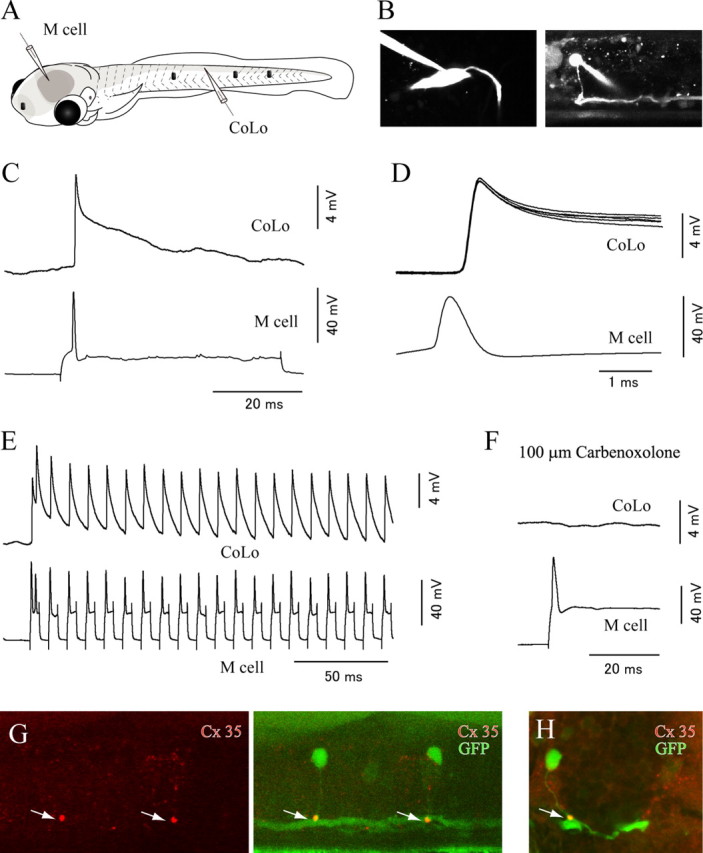
The Mauthner cell makes electrical synapses onto CoLo neurons. A, A schematic illustration of the paired patch recordings between an M-cell and a CoLo neuron. The black dots represent tungsten holding pins. B, Images of the M-cell (left) and the CoLo neuron (right) after the electrophysiological recordings shown in C–F. Larva at 4 dpf. C, The current-evoked spike of the M-cell led to a fast and sharp depolarizing response (∼10 mV in amplitude) in the CoLo neuron. This sharp depolarizing response represents a spike in the CoLo neuron (see Fig. 5 and Results). D, Five superimposed traces of CoLo spikes evoked by M-cell spikes. The traces show short, constant latency spikes. Only one spike in the M-cell is shown for simplicity. Traces of voltage responses in the CoLo neuron are aligned with the peak of the spikes in the M-cell. E, Responses of the CoLo neuron on 100 Hz spikes of the M-cell. CoLo spikes perfectly followed M-spikes with the same amplitude in each spike. F, Response of the CoLo neuron was eliminated after treatment with 100 μm Corbenoxolone (a gap junction blocker) for 15 min. G, Lateral view of immunostaining with Cx35. A stacked image of confocal optical sections. The left shows staining of Cx35, whereas the right shows a merged image of Cx35 and GFP. The intense Cx35 signals (arrows) are observed at the contact sites between CoLo axons and the M-axon. H, A cross section. The arrow shows an intense signal of Cx35.
