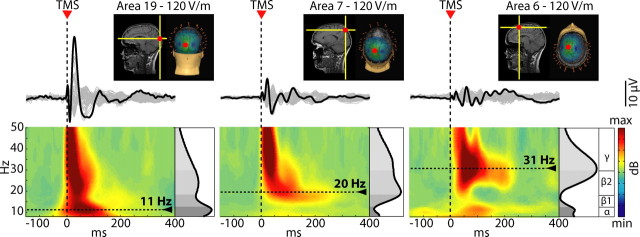
Figure 1.
TMS induces global EEG oscillations that are specific for the stimulated site. The insets illustrate the three cortical sites targeted by TMS (hot spot on the individual MRI) in one subject. The traces below represent butterfly plots, where the black trace highlights the electrode directly underlying the stimulator. The bottom panels show the ERSP patterns calculated globally on the scalp (average of all electrodes). The gray scale graph plotted at the right of each ERSP depicts the power spectrum profile induced during the first 200 ms after TMS. The dotted lines highlight the frequency with maximum power, the natural frequency. TMS elicited early γ components immediately followed by prominent α-band oscillations after occipital stimulation, β-band oscillations after parietal stimulation, and fast β/γ oscillations after perturbation of frontal cortex.