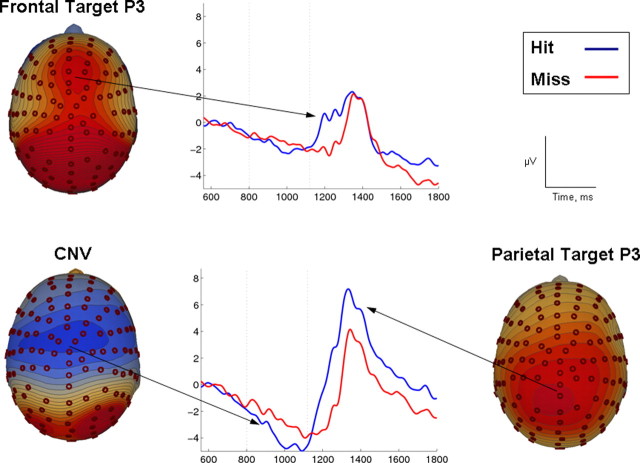
Figure 2.
Immediate target processing. Grand average ERP waveforms and scalp topographies focused on the target detection interval and averaged separately for hits and misses. Scalp topographies show potential distribution for hits. Although the waveforms were time-locked to the onset of the target frame (time point 0), a target frame cannot be identified until its duration passes that of a standard frame (800–1120 ms, referred to as the target interval and highlighted by dashed vertical lines). The target interval elicited a central negativity between 600 and 1100 ms (CNV, bottom-left) and a late positive wave with frontocentral (1200 ms, frontal target P3; top) and parietal maxima (1400 ms, Parietal Target P3; bottom-right). Each of these components was reduced on miss trials.