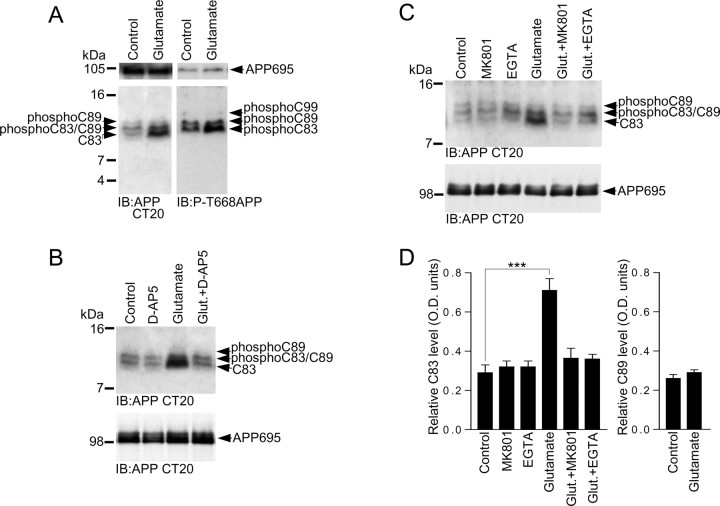
Figure 4.
Glutamate increases α-CTF (C83) levels in primary cultured cortical neurons. A, Primary cultured cortical neurons at 10 DIV were treated with vehicle (control) or 20 μm glutamate for 15 min followed by immunoblotting of neuronal lysates with APP Abs CT20 or phospho-APP (thr668) (P-T668APP). B, Primary cultured cortical neurons at 10 DIV were treated with vehicle (control), 100 μm d-AP5, 20 μm glutamate, or 20 μm glutamate in the presence of 100 μm d-AP5 (Glut.+D-AP5) for 15 min followed by immunoblotting of neuronal lysates with APP Ab CT20. C, Primary cultured cortical neurons at 10 DIV were treated with vehicle (control), 2 μm MK801, 2 mm EGTA, 20 μm glutamate, 20 μm glutamate in the presence of 2 μm MK801 (Glut.+MK801), or 20 μm glutamate in the presence of 2 mm EGTA (Glut.+EGTA) for 15 min followed by immunoblotting of neuronal lysates with APP Ab CT20. D, C83 levels in cortical neurons treated with vehicle (control), MK801, EGTA, glutamate, glutamate in the presence of MK801 (Glut.+MK801), and glutamate in the presence of EGTA (Glut.+EGTA), and C89 levels in cortical neurons treated with vehicle (control) or glutamate, were analyzed by ECL protein band densitometry using calibrated ImageJ software. Each column is the mean ± SEM of six independent experiments (n = 6; ***p < 0.001, control vs glutamate, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test).