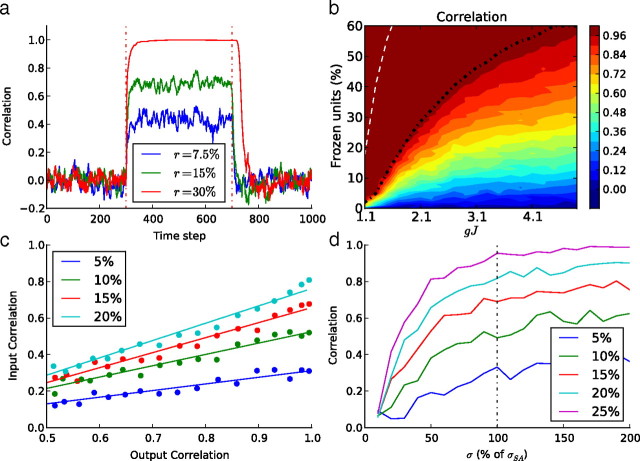
Figure 9.
a, Kinetics of the normalized cross-correlation between the target activity and the response of neural fields as a function of time, before, during, and after the frozen stimulation, for three different ratios of frozen neural fields. In this example, gJ = 2.1. b, Steady-state values of the cross-correlation between target and free-running activities measured as a function of the ratio of frozen neural fields (vertical axis) and the network parameter gJ (horizontal axis). The black dotted line is the full convergence limit (CC > 0.99) and the white dotted line the limit under which the free subnetwork, without any stimulation, is still chaotic. c, Normalized cross-correlation for several percentages of frozen units and for several amounts of noise added (in percentage of σSA) to an ongoing pattern. d, Normalized cross-correlation when a surrogate Gaussian noise with a standard deviation expressed in percentage of σSA is used as a stimulation instead of a real pattern. In both cases, the network parameter was gJ = 2.1.