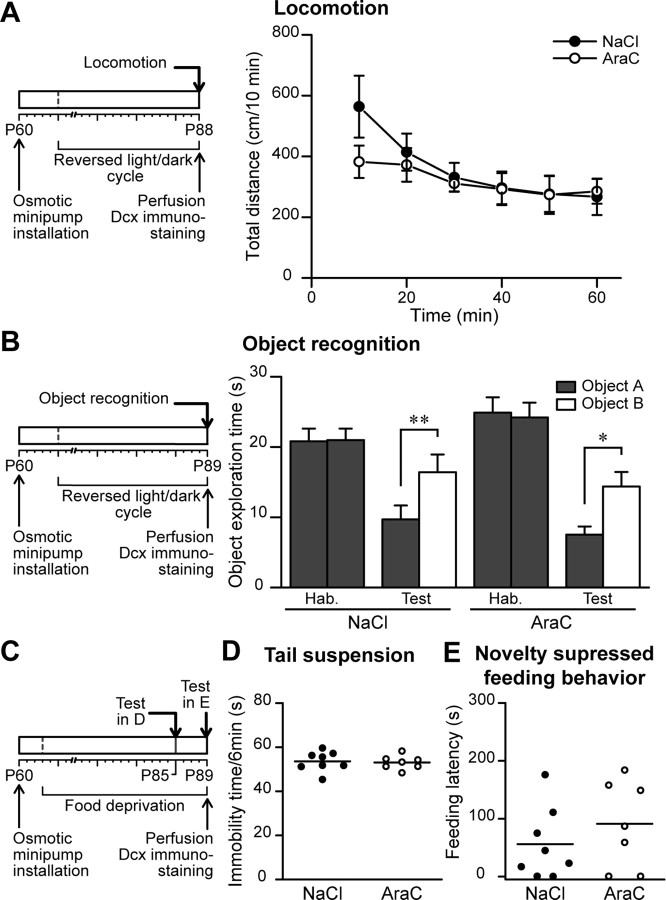
Figure 6.
AraC treatment does not affect general locomotor and exploratory activities, anxiety, and motivation of the mouse. A, Left, Experimental design used for the locomotion test. Note that the mice were kept in a reversed light/dark cycle and tested 28 d after pump installation. Right, Results at different time points of the 60 min spontaneous locomotion test. Mice infused with NaCl or with AraC travel the same distance in the locomotion test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 9 and 8 animals for control and AraC-treated group). B, Left, Experimental design used for the object recognition test. The animals were tested 29 d after osmotic minipump installation. Right, Object exploration time in seconds for animals presented with two identical (habituation phase) or two different (test phase) objects. Mice with ablated neurogenesis are able to recognize the object in the same manner as control animals. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 9 animals per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; Student's t test. C, Experimental design used for the tail suspension test (D) and novelty-suppressed feeding behavior test (E). Mice used in these test were food deprived. D, Immobility times of NaCl- and AraC-treated mice during a 6 min tail suspension test. Each dot represents the immobility time (in seconds) for one animal. Horizontal bars represent the mean values for all the animals for control and AraC-treated conditions (n = 8 and 7 animals, respectively). E, Feeding latencies of mice (in seconds) submitted to a novelty-suppressed feeding behavior test. Each dot represents the feeding latency for one animal, whereas horizontal bars represent the mean value for all the animals from control and AraC-treated conditions (n = 8 and 7 animals, respectively).