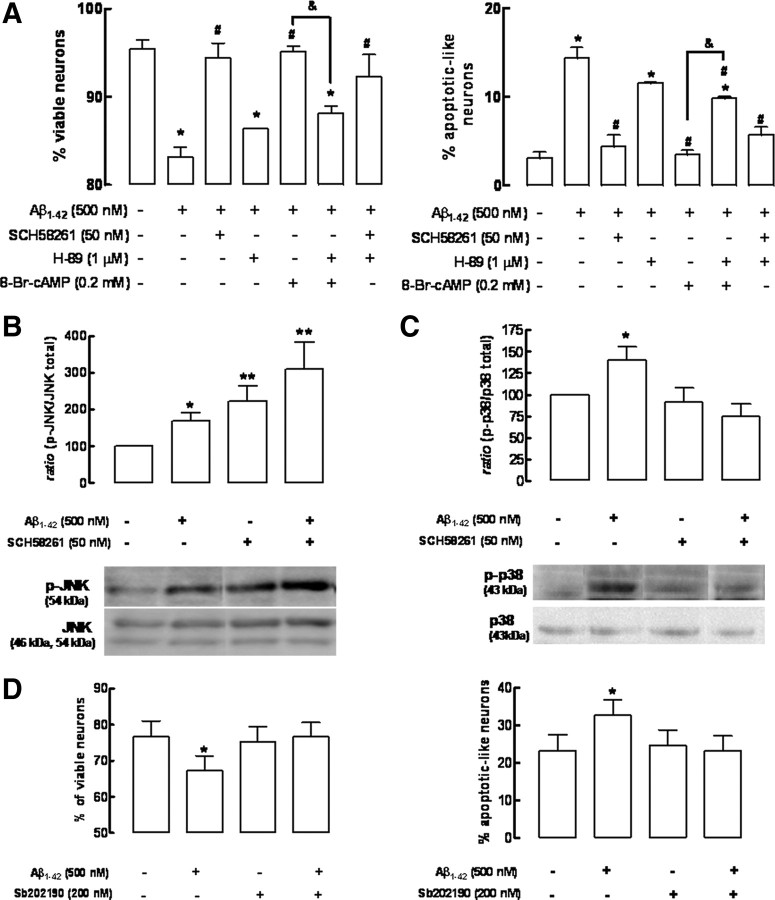
Figure 7.
The neuroprotection afforded by blockade of adenosine A2A receptors against Aβ1-42-induced neurotoxicity involves the p38 MAPK rather than the cAMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway. Hippocampal neurons were preincubated with the A2AR antagonist SCH58261 (50 nm) or with the cAMP analog 8-Br-cAMP (200 μm) 15 min before addition of 500 nm Aβ1-42. All inhibitors tested were added 30 min Aβ1-42. A, Neuroprotection by SCH58261 does not involve the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway since the PKA inhibitor H-89 (1 μm) prevents the neuroprotection afforded by 8-Br-cAMP, but fails to modify the neuroprotection afforded by SCH58261, as evaluated after 24 h of exposure to Aβ1-42 (*p < 0.05 vs control #p < 0.05 vs Aβ1-42; &p < 0.05 vs Aβ1-42 + 8-Br-cAMP). B, C, Aβ1-42 triggered the activation of JNK (B) and p38 MAPK (C), evaluated by their degree of phosphorylation after 2 h, and SCH58261 enhanced JNK phosphorylation, whereas it blocked p38 MAPK phosphorylation (data are mean ± SEM from 6 independent cultures; *p < 0.05 vs control; **p < 0.05 vs effect of Aβ). D, The p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190 prevents neuronal death induced by Aβ1-42 (data are mean ± SEM from 5 independent cultures; *p < 0.05 vs control).