Figure 2.
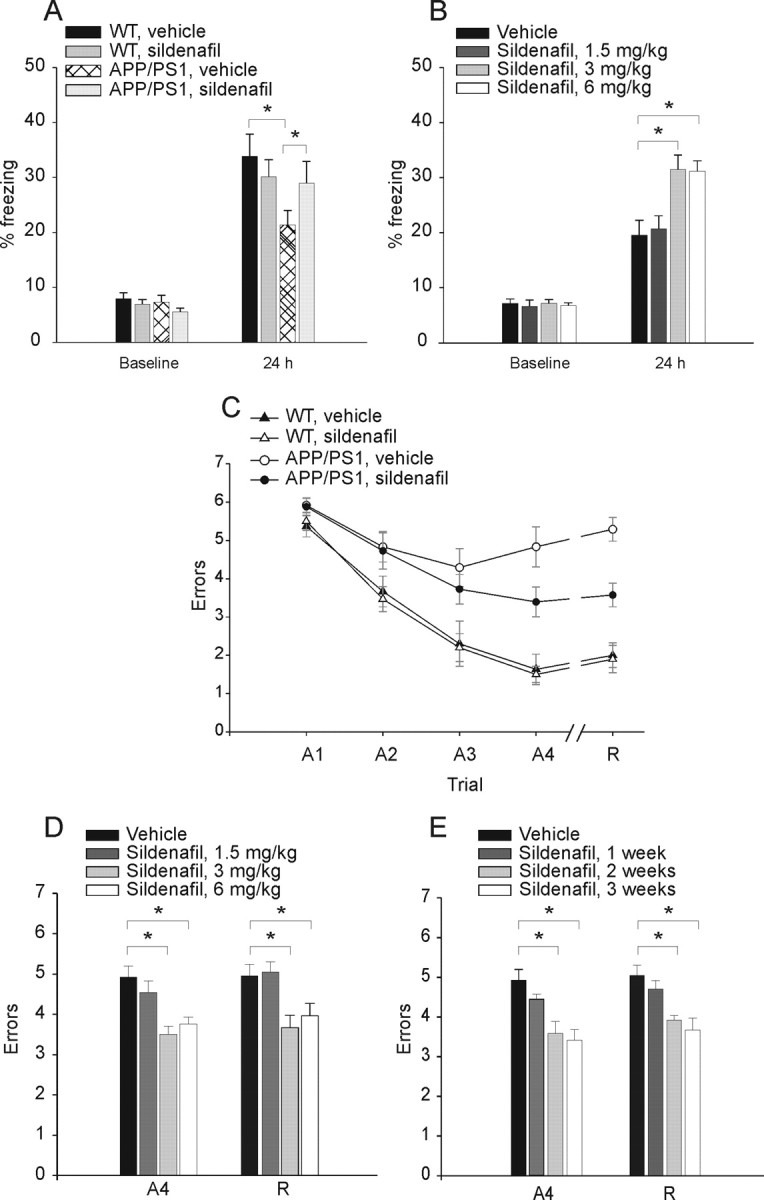
Sildenafil ameliorates cognitive function in 3-month-old APP/PS1 mice. A, Sildenafil (3 mg/kg, i.p.) improves contextual fear conditioning in 3-month-old APP/PS1 mice. APP/PS1 and WT littermates treated with sildenafil or vehicle show no difference in freezing before training (baseline; one-way ANOVA among the 4 groups: F(3,79) = 2.39, p = 0.07), whereas contextual fear conditioning performed 24 h after training shows a reduction of freezing responses in APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle compared with vehicle-treated WT littermates [the freezing time of vehicle-treated APP/PS1 mice was ∼63% of vehicle-treated WT mice; n = 21 (12 males and 9 females), WT littermates, n = 20 (11 males and 9 females), F(1,39) = 6.64, p = 0.01]. The freezing response is improved in sildenafil-treated APP/PS1 mice [the freezing time of sildenafil-treated APP/PS1 mice was ∼87% of vehicle-treated WT mice: n = 22 (12 males and 10 females); F(1,40) = 0.73, p = 0.39]. Sildenafil has no effect on the freezing responses of WT mice compared with vehicle-treated WT littermates [∼89% of vehicle-treated WT mice: n = 20 (11 males and 9 females); F(1,38) = 0.52, p = 0.47]. B, The minimum concentration of sildenafil needed to improve contextual fear memory in APP/PS1 mice is 3 mg/kg. A concentration of 1.5 mg/kg does not improve freezing, whereas 6 mg/kg has the same effect as 3 mg/kg [1.5 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females) vs vehicle-treated animals, n = 14 (7 males, 7 females), F(1,20) = 0.82, p = 0.375; 3 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females), F(1,20) = 11.58, p = 0.003; 6 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females), F(1,20) = 8.48, p = 0.009]. C, Sildenafil (3 mg/kg, i.p.) improves spatial working memory in 3-month-old APP/PS1 mice. APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle do not learn the position of the hidden platform compared with vehicle-treated WT littermates [APP/PS1: n = 8 (4 males and females); WT: n = 10 (5 males and females); two-way ANOVA: (F(1,16) = 39.66, p < 0.0001, and planned comparisons show that the two groups are significantly different at the second acquisition trial (A2) (p = 0.05), A3 (p = 0.02), A4, and recall trial (R) (p < 0.0001)]. However, treatment with sildenafil ameliorates the performance of double transgenic littermates compared with vehicle-treated APP/PS1 [n = 11 (6 males and 5 females); F(1,17) = 5.99, p = 0.02, and planned comparisons show that the 2 groups are significantly different at trial A4 (p = 0.03) and R (p = 0.001)]. Sildenafil does not affect the performance of WT mice compared with vehicle-treated WT mice [sildenafil: n = 10 (5 males and females); F(1,18) = 0.09, p = 0.76]. D, The minimum concentration of sildenafil needed to improve spatial working memory in APP/PS1 mice is 3 mg/kg for 3 weeks. A concentration of 1.5 mg/kg does not improve RAWM performance, whereas 6 mg/kg has the same effect as 3 mg/kg [1.5 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females) vs vehicle-treated animals: n = 14 (7 males, 7 females), F(1,20) = 0.82, p = 0.375 and F(1,20) = 0.05, p = 0.824 for A4 and R, respectively; 3 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females), F(1,20) = 11.58, p = 0.003 and F(1,20) = 11.36, p = 0.003; 6 mg/kg sildenafil: n = 8 (4 males, 4 females), F(1,20) = 8.48, p = 0.009 and F(1,20) = 7.12, p = 0.015]. E, Summary graph showing that the minimum time needed for sildenafil to have a positive effect on spatial working memory in APP/PS1 mice is 2 weeks, with a concentration of 3 mg/kg [1 week: F(1,20) = 1.81, p = 0.19 and F(1,20) = 0.82, p = 0.386 for A4 and R, respectively; 2 weeks: F(1,20) = 9.69, p = 0.005 and F(1,20) = 10.35, p = 0.004; 3 weeks: F(1,20) = 13.19, p = 0.002 and F(1,20) = 11.36, p = 0.003; n = 8 (4 males, 4 females) for each condition].
