Figure 1.
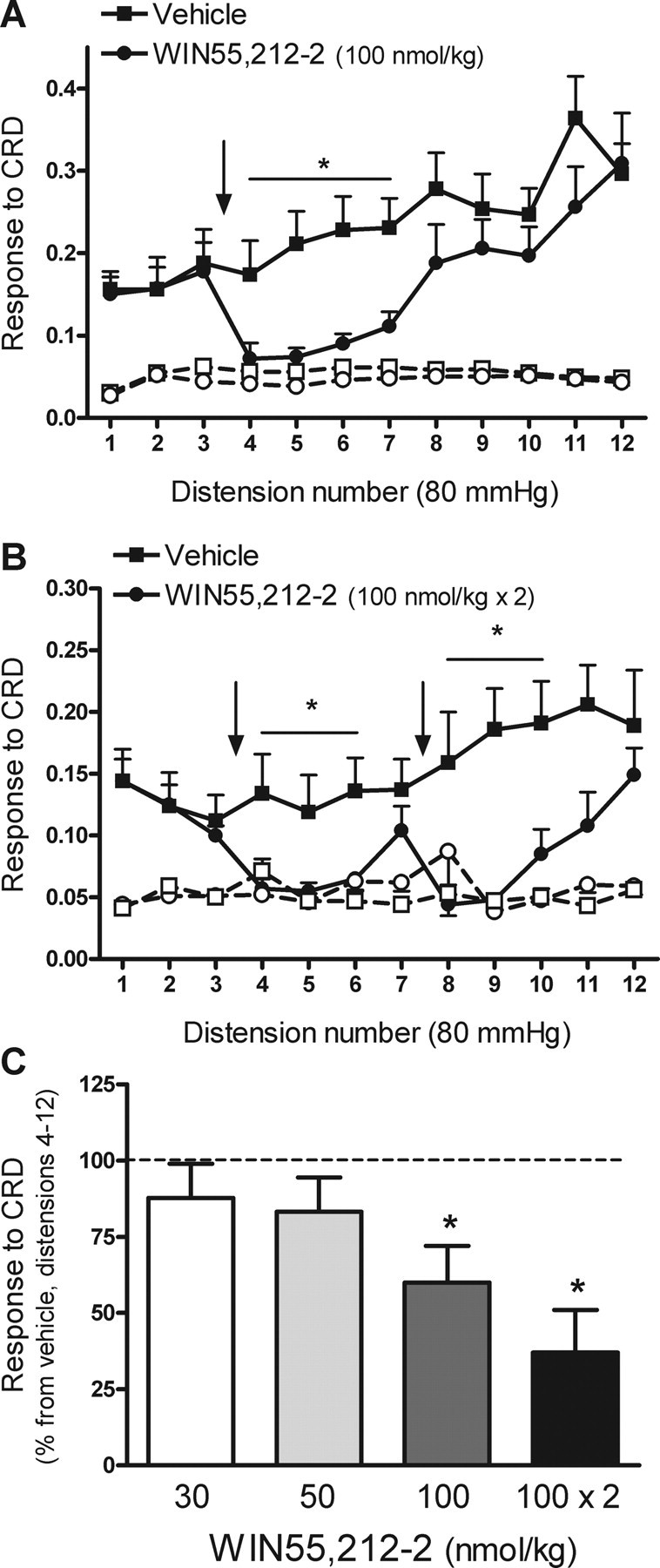
Effects of WIN55,212-2 on repetitive noxious CRD-evoked pain related responses in rats. A, Effects of WIN55,212-2 (100 nmol/kg) or vehicle (1 ml/kg), administered intravenously between distensions 3 and 4, on CRD-evoked pain related responses. Graphs with open symbols and broken lines correspond to the basal activity of the abdominal musculature between distensions. The arrow indicates the point of WIN55,212-2 or vehicle administration. Data are mean ± SEM of eight animals per group. *p < 0.05 versus corresponding response in the vehicle-treated group. B, Effects on pain-related responses to CRD of repeated administration of WIN55,212-2 (100 nmol/kg) between distensions 3 and 4 and 7 and 8 (as indicated by the arrows). Graphs with open symbols and broken lines correspond to the basal activity of the abdominal musculature between distensions. Data are mean ± SEM of seven animals per group. *p < 0.05 versus corresponding response in the vehicle-treated group. C, Overall effects of WIN55,212-2 (% inhibition vs the response in the vehicle group, set up at 100%; broken line) on pain-related responses during distensions 4–12 of the noxious CRD protocol. Data are mean ± SEM of 4–8 animals per group. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle.
