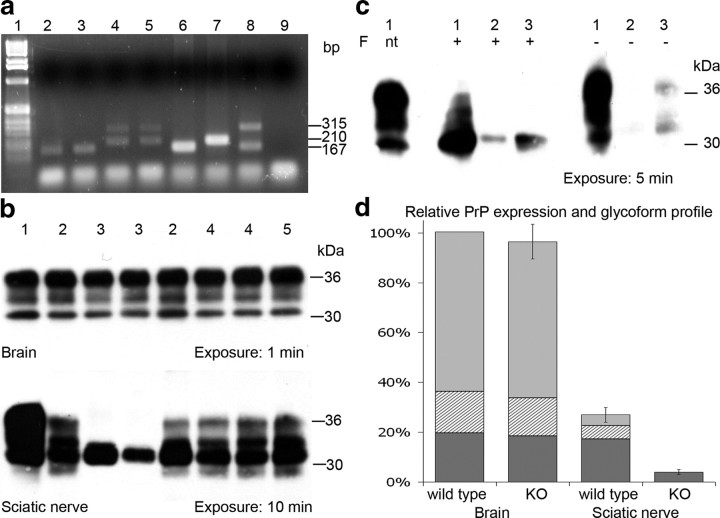
Figure 1.
a, PCR analysis of DNA extracted from sciatic nerve tissue revealing Cre-mediated recombination in Schwann cell PrP knock-out mice only. Lanes: 1, 1 kb DNA ladder (Invitrogen); 2, wt sciatic nerve; 3, Cre control sciatic nerve; 4 and 5, Schwann cell PrP knock-out sciatic nerve; 6, wt tail tip PCR control; 7, PrPfl/fl tail tip PCR control; 8, PrPfl/wt Cre-Deleter tail tip PCR control; 9, H2O PCR control. Band sizes indicated in base pairs: 167 bp 5′ region upstream of PrP exon 3 (wt allele); 210 bp 5′ region upstream of Prnp exon 3 including loxP site (PrPfl allele); 315 bp 5′ and 3′ PrP after Cre-mediated excision of exon 3 (Cre-mediated recombined PrPfl allele). b, Western blot analysis of PrP expression in brain (top) and sciatic nerve (bottom) tissue using anti-PrP antibody 7A12. Samples: 1, 129/Ola brain; 2, floxed PrP control; 3, Schwann cell PrP knock-out, revealing reduction of total PrP and loss of PrP glycoforms in PNS tissue; 4, Cre control; and 5, nontransgenic control. Approximate protein molecular weight markers given in kilodaltons. c, Western blot analysis of wild-type brain (1) and sciatic nerve (3) and Schwann cell PrP KO sciatic nerve (2) following N-glycosidase F (F) treatment (+), when not treated (nt), or without enzyme treatment (−). d, Relative PrP expression and glycoform profile in brain and sciatic nerve of wild-type mice and Schwann cell PrP knock-out mice, normalized to wild-type brain expression level; diglycosylated (light gray), monoglycosylated (hatched), and unglycosylated (dark gray) species are indicated. Error bars represent total expression level ± SEM.