Figure 3.
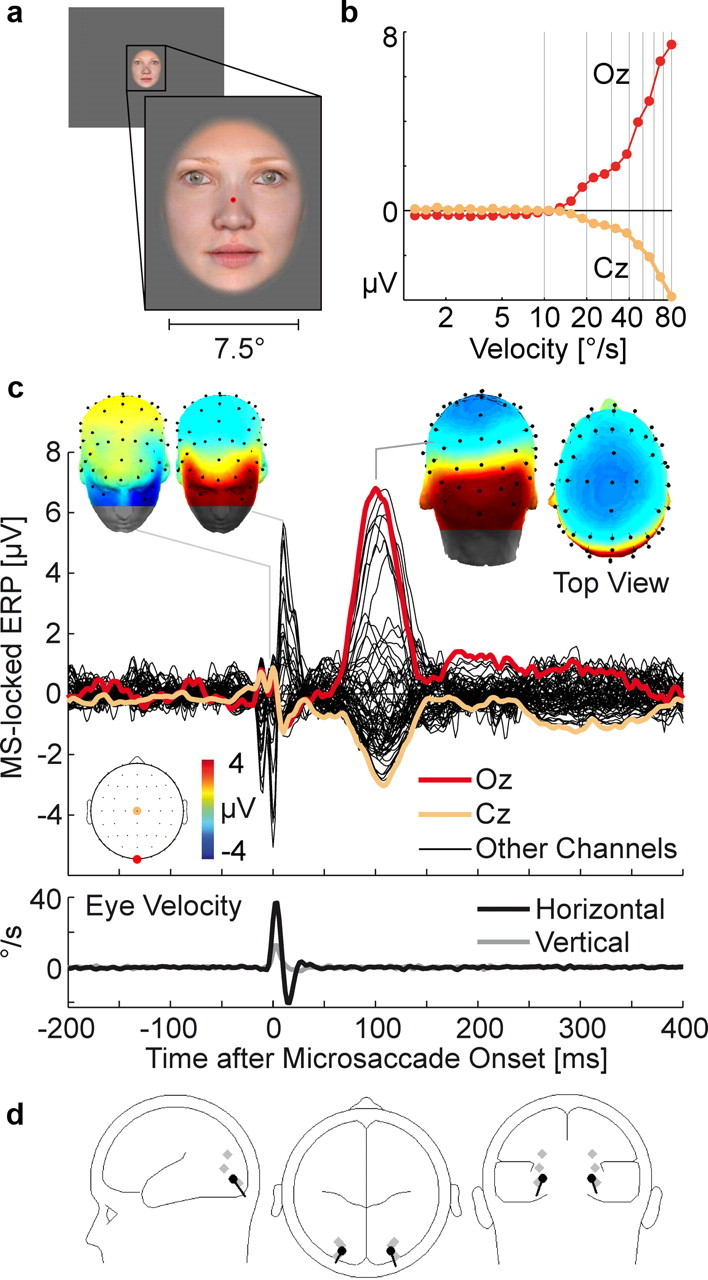
Microsaccade-related potentials during face fixation. a, Example stimulus. b, EEG voltage as a function of instantaneous eye velocity 100 ms earlier. c, Grand average microsaccade-locked ERP. The double spike at microsaccade onset is due to an individual subject for whom the SP preceded movement onset by 10 ms. This caused a doubled SP in the grand average ERP (see supplemental Fig. S3, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). d, Dipole model at the peak of the MLR.
