Figure 3.
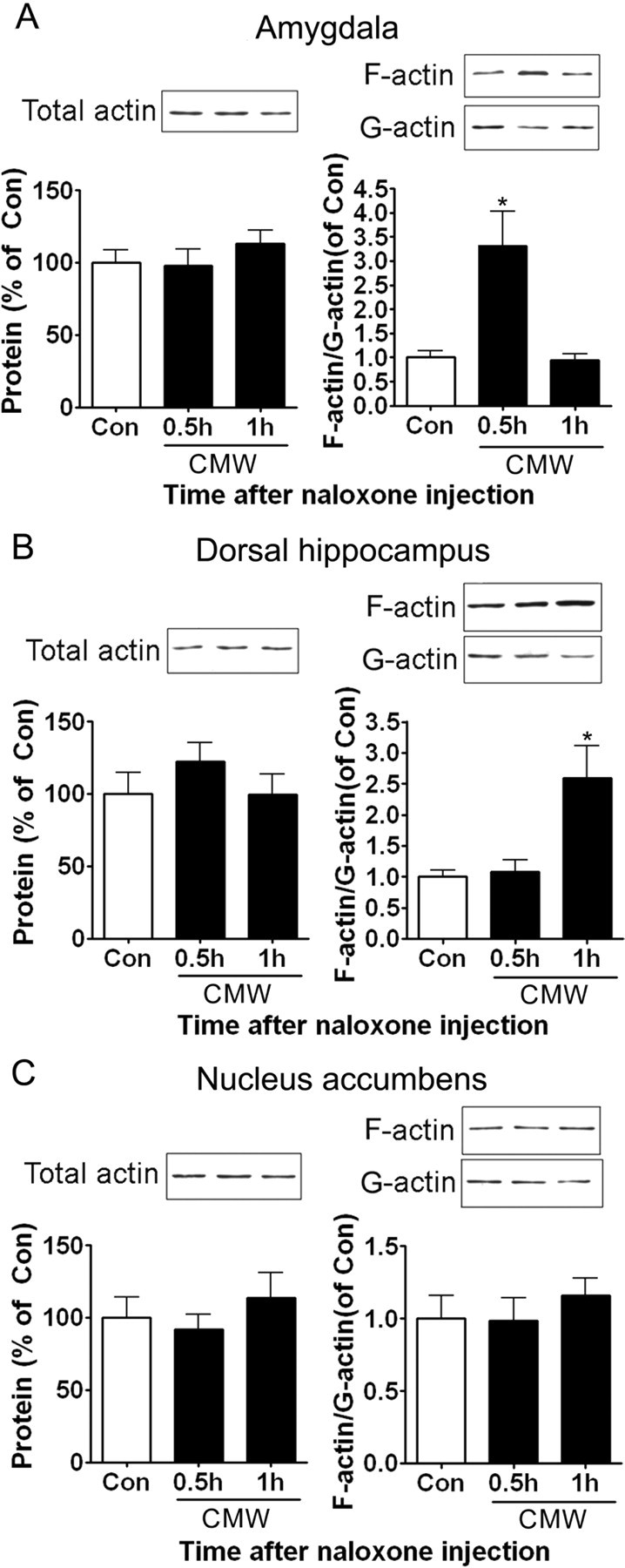
Effects of conditioned naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal on actin rearrangements in the amygdala, the DH, and the NAc. A, Conditioned morphine withdrawal induced an increase in the ratio of F-actin to G-actin in the amygdala at 0.5 h after naloxone injection. B, Conditioned morphine withdrawal induced an increase in the ratio of F-actin to G-actin in the DH at 1 h after naloxone injection. C, Conditioned morphine withdrawal failed to induce an increase in the ratio of F-actin to G-actin in the NAc. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). *p < 0.05, compared with the corresponding saline-treated control group, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. Con, Control; CMW, conditioned morphine withdrawal.
